Carbon fiber and aluminum fiber are two distinct materials that find extensive applications in various industries. Their unique properties make them desirable choices for a wide range of products and components. Understanding the key differences between carbon fiber and aluminum fiber is crucial in determining the most suitable material for specific applications. This article provides an insightful analysis of six significant differences between carbon fiber and aluminum fiber, shedding light on their composition, strength, weight, corrosion resistance, thermal conductivity, and cost. Hope to help you choose the proper material for your application.

Carbon fiber and aluminum fiber are both materials used in various industries for their unique properties and characteristics. Here are the key differences between carbon fiber and aluminum fiber:
Composition and Structure of Carbon fiber and Aluminum Fiber
Carbon Fiber: Carbon fiber is composed of thin, strong strands of carbon atoms, typically arranged in a crystalline structure. The fibers are made through a complex process of heating and stretching precursor materials, such as polyacrylonitrile (PAN) or pitch.
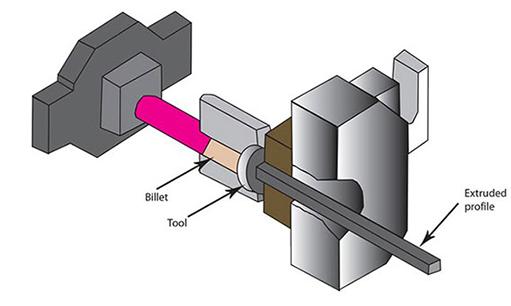
Aluminum Fiber: Aluminum fiber is composed of pure aluminum metal in a fibrous form. It is typically produced by extrusion or other mechanical processes to create long, thin aluminum strands.
Strength and Stiffness of Carbon fiber and Aluminum Fiber
Carbon Fiber: Carbon fiber is renowned for its exceptional strength and stiffness-to-weight ratio. It is stronger than steel but significantly lighter. Carbon fiber composites exhibit high tensile strength, providing excellent resistance to bending and deformation.
Aluminum Fiber: Aluminum fiber is relatively strong but not as strong as carbon fiber. It has a lower tensile strength and stiffness compared to carbon fiber. However, aluminum is still widely used in engineering applications due to its favorable strength-to-weight ratio among metals.
Weight of Carbon fiber and Aluminum Fiber
Carbon Fiber: Carbon fiber is extremely lightweight due to its low density. It offers significant weight savings compared to traditional materials like steel or aluminum. The lightweight nature of carbon fiber is advantageous in applications where weight reduction is critical, such as aerospace, automotive, and sporting goods industries.
Aluminum Fiber: While aluminum is lightweight compared to many other metals, it is denser than carbon fiber. Aluminum fiber components will typically be heavier than equivalent carbon fiber components, although still lighter than materials like steel.
Corrosion Resistance of Carbon fiber and Aluminum Fiber
Carbon Fiber: Carbon fiber itself is highly corrosion resistant, as carbon does not easily react with most chemicals. However, carbon fiber composites may still be vulnerable to degradation when exposed to certain corrosive environments, especially if the resin matrix used is not corrosion resistant.
Aluminum Fiber: Aluminum has good corrosion resistance, particularly when exposed to air or water. It forms a protective oxide layer on the surface, which helps prevent further corrosion. However, aluminum can corrode in acidic or alkaline environments.
Thermal Conductivity of Carbon fiber and Aluminum Fiber
Carbon Fiber: Carbon fiber has low thermal conductivity, meaning it is a poor conductor of heat. This property makes it suitable for applications requiring insulation or thermal resistance.
Aluminum Fiber: Aluminum has high thermal conductivity, making it an excellent conductor of heat. It quickly transfers heat, which can be advantageous in applications where heat dissipation is desired.
Cost of Carbon fiber and Aluminum Fiber
Carbon Fiber: Carbon fiber is generally more expensive than aluminum fiber. The production process and raw material costs contribute to the higher price of carbon fiber composites.
Aluminum Fiber: Aluminum fiber is relatively more cost-effective compared to carbon fiber. Aluminum is a widely available and less expensive material, making it a popular choice in various applications.
The choice between carbon fiber and aluminum fiber depends on the specific requirements of the application, including factors such as desired strength, weight savings, corrosion resistance, thermal properties, and budget considerations.
CHAL has successfully developed high-precision aluminum ultra-fine fiber, aluminum fiber for cable, aluminum fiber wire, aluminum capillary tube (small diameter tube) and puts these products into the market in 2011, our quality is highly regarded by customers. If you are looking for aluminum fiber, please feel free to contact us.
Related Products
Related Articles