Aluminum profiles are widely used in modern industry, construction and daily life. From the frame structure of buildings to the shell of industrial equipment, to the production of furniture, aluminum profiles play an important role. Selecting the right aluminium section size is critical to ensuring structural integrity, functionality, and cost-efficiency. This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of aluminum sections, their measurement, and the key factors to consider when choosing the right size for your specific needs.
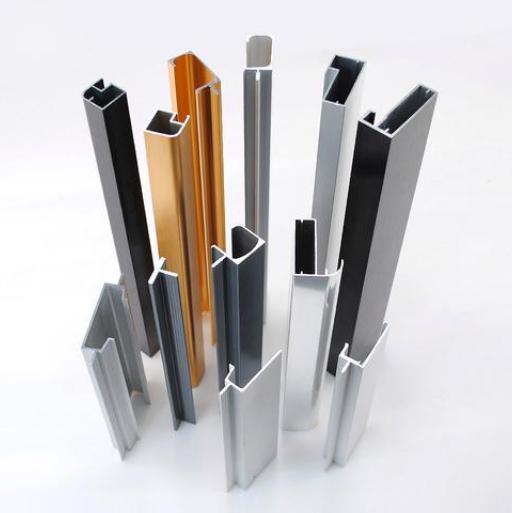

What Are Aluminium Sections?
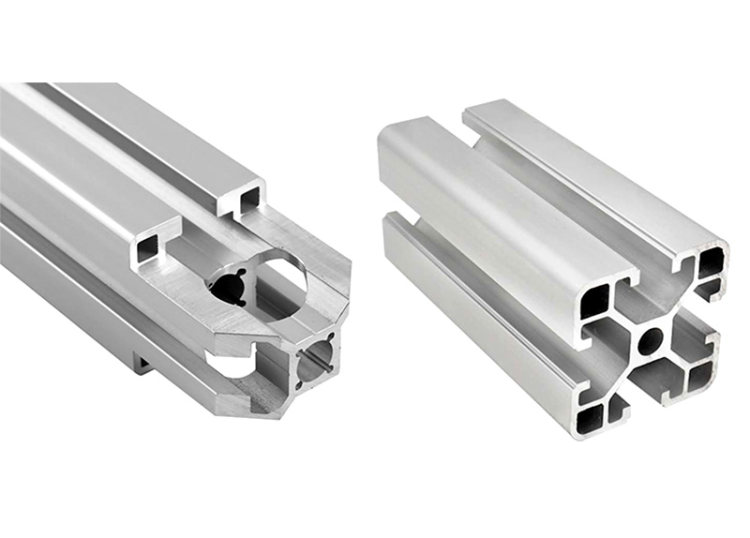
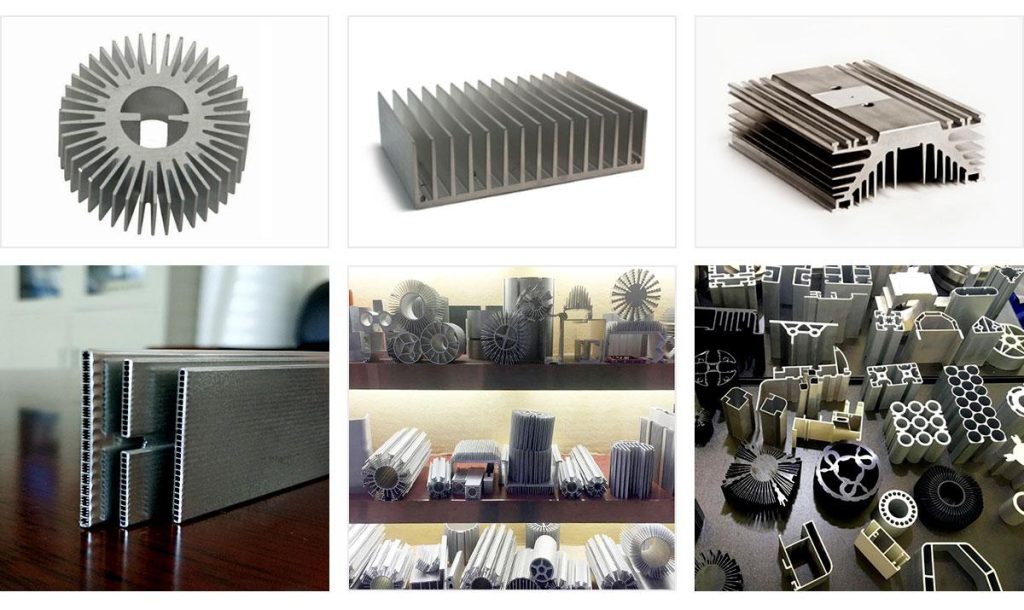
Aluminum sections are a type of material with a specific cross-sectional shape that is made from aluminum as the main raw material through an extrusion process. Aluminum sections are favored in many fields due to its light weight, corrosion resistance, high strength, and good plasticity. During the production process, aluminum ingots are heated, extruded, and shaped into profiles of different shapes and sizes.
Common Section Types
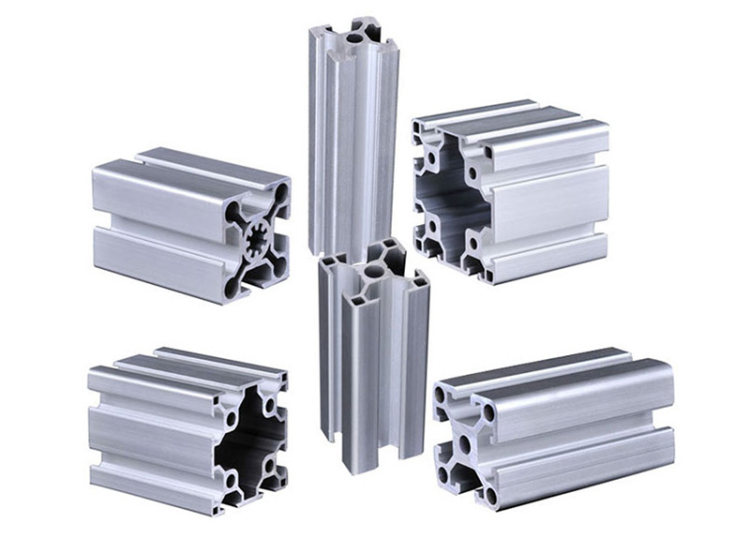
Extruded Profiles: These are the most common types, manufactured by forcing molten aluminum through a die to create a specific shape. Some common extruded profiles include:
- I-beams: Featuring a top and bottom flange connected by a web, providing excellent strength and stiffness.
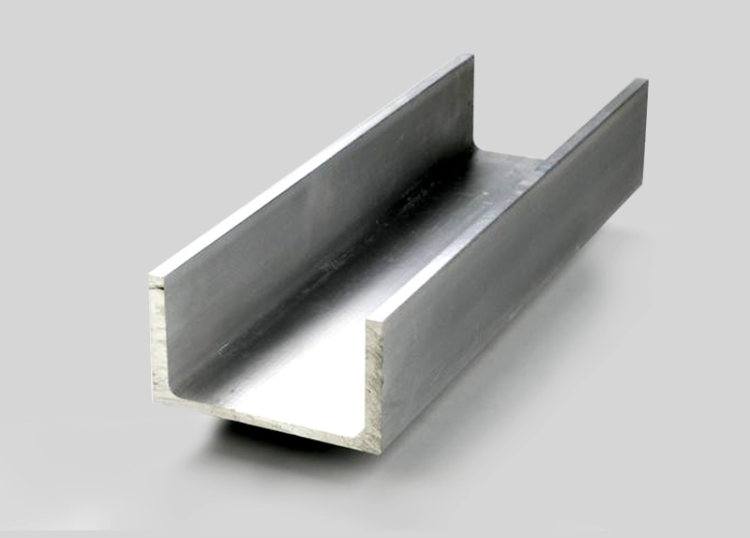
- Channels: Similar to I-beams but with only one flange, often used for structural support.
- Angles: Formed by two intersecting legs at a 90-degree angle, commonly used for framing and bracing.
- T-sections: Shaped like the letter “T,” offering a combination of strength and versatility.
- Square and Rectangular Tubes: Hollow sections with high strength-to-weight ratios.
- Round Tubes: Ideal for applications requiring high torsional strength and resistance to bending.
Plate and Sheet: These are flat, rolled aluminum products available in various thicknesses. They are widely used for cladding, fabrication, and general construction purposes.
Forgings: These are aluminum components shaped by applying pressure to the metal, resulting in high strength and complex shapes.
The diversity of aluminum sections provides a wealth of options for various applications, but different types and sizes of profiles have different applicability in different scenarios. Next, let’s take a look at the main dimensions and measurement methods of aluminum sections.

How to Measure Aluminium Sections?
Accurate measurement is vital to ensure the aluminium section fits the intended application. Know the key dimensions and units are essential before measure.
Key Dimensions
The key dimensions of an aluminum section determine its strength, stiffness, and weight-carrying capacity. These dimensions typically include:
- Width: The horizontal measurement of the section.
- Depth/Height: The vertical measurement, often critical for load-bearing capacity.
- Thickness: The wall thickness, impacting durability and weight.
- Inner/Outer Diameter: For hollow sections, these measurements define their capacity and strength.
- Radius/Fillet: The curvature at the corners of the section, which can significantly influence stress distribution.
By understanding these common types and dimensions, you can narrow your selection to what suits your project requirements.
Measurement Units
Aluminium sections are typically measured in millimeters (mm) or inches. Metric units are more common globally, while inches dominate in certain regions like the US.
Weight is often expressed in kilograms per meter (kg/m) for structural applications.

Measurement Methods for Aluminum Sections
Cross-Sectional Dimension Measurement:
- Wall Thickness: Use a caliper to accurately measure the wall thickness of the aluminum section. Place the caliper jaws perpendicular to the wall and read the measurement.
- Non-Wall Thickness Dimensions: For dimensions like the width of a channel in a channel-shaped section, use a caliper or micrometer. Ensure the measuring tool is perpendicular to the section’s surface and the measurement point is accurate.
- Angle: Use an angle gauge to measure the angle of the aluminum section. Align the sides of the gauge with the section’s angled edges and read the angle.
- Fillet Radius and Corner Radius: Use an R-gauge to measure these radii. Match the different radius curves of the R-gauge to the section’s fillet or corner and find the best fit. The corresponding radius value is the fillet or corner radius.
Measurement of Curvature:
- Longitudinal Curvature: Place the aluminum section on a horizontal platform and let it stabilize under its own weight. Use a feeler gauge to measure the maximum gap between the bottom surface and the platform along the length.
- Longitudinal Waviness (or Hard Bend): Place a 300mm straight edge along the wave or hard bend and use a feeler gauge to measure the maximum gap between the straight edge and the section’s surface.
- Longitudinal Side Bend: Place the largest plane of the section on a platform. Draw a straight line on the platform through the two end points of the side. Use a feeler gauge to measure the maximum gap between the straight line and the side. Alternatively, place a 1m straight edge along the side and measure the maximum gap.
Measurement of Twist: Place the aluminum section on a platform with one end firmly against it. Let the section stabilize under its own weight. Use a feeler gauge to measure the difference in the gaps between the two end points of the raised end of the section and the platform.
Measurement of Taper and Length: Use a precision steel tape measure or ruler to measure the taper and length.
Accurate measurement is crucial for ensuring the quality and correct use of aluminum sections. Using appropriate measuring units and correct measurement methods guarantees the accuracy and reliability of aluminum sections during processing, installation, and use.

Factors to Consider When Choosing Aluminum Extrusion Sizes
Factors Influencing Extrusion Size Selection
- Load-bearing Capacity: If the aluminum extrusion is required to support significant weight or pressure, such as acting as a load-bearing beam in a building structure or supporting heavy components in industrial equipment, a larger wall thickness and cross-sectional area are necessary to ensure sufficient strength and stability.
- Installation Space: In confined spaces, like narrow equipment compartments or compact building layouts, the extrusion size must be compatible with the limited installation space. This requires selecting an appropriate size that meets functional requirements while avoiding installation difficulties due to excessive size.
- Aesthetic Requirements: In applications with high aesthetic demands, such as architectural decoration and high-end furniture, the extrusion size may need to be selected based on the overall design aesthetics. For example, thinner extrusions may be more suitable for creating a clean, modern appearance.
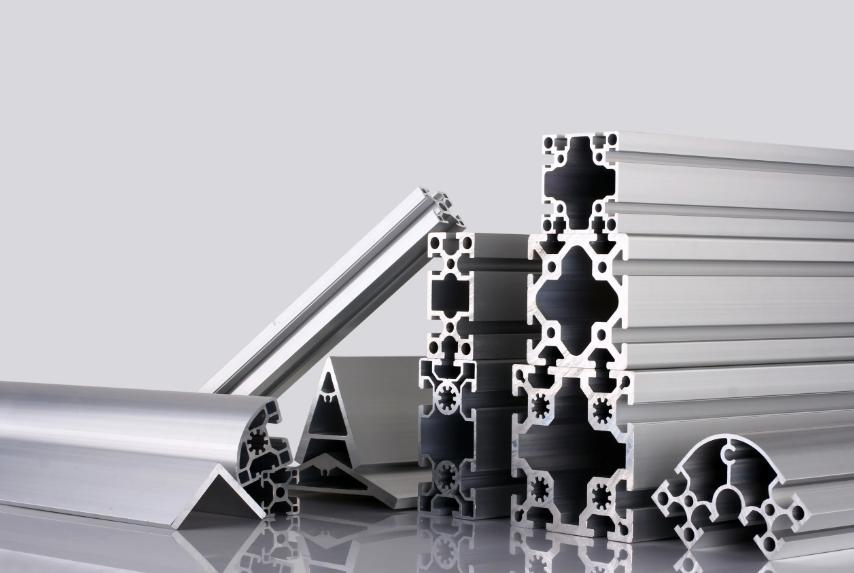

Selection Methods
- Needs Analysis: First, clearly define the purpose and requirements of the aluminum extrusion, determining key factors such as the load to be carried, operating environment, and appearance requirements.
- Reference Standards and Specifications: Refer to industry standards and specifications for requirements and recommended values for aluminum extrusion sizes in similar applications. For example, the construction industry has building structure design codes that specify the use of aluminum extrusions in buildings.
- Testing and Simulation: In complex applications, mechanical tests or computer simulations can be used to evaluate the performance of different extrusion sizes, allowing for the selection of the most suitable size.
Selecting the appropriate aluminum extrusion size is a comprehensive process that involves considering multiple factors. Only by fully considering load-bearing capacity, installation space, aesthetic requirements, and other factors, and by employing scientific selection methods, can the performance and effectiveness of the aluminum extrusion in its application be optimized.
From understanding the basic concept of aluminum sections, to accurate measurement methods, to selecting the appropriate size based on various factors, each link is interrelated. Correct measurement can ensure the quality of aluminum sections and meet the requirements of use, while the appropriate size selection can ensure that aluminum sections can perform at their best in different application scenarios. Whether in industrial production, construction projects or various aluminum section application scenarios in daily life, the measurement and selection of aluminum section sizes should be taken seriously. Need any advices about aluminum sections measurement or choosing, please feel free to contact CHAL.