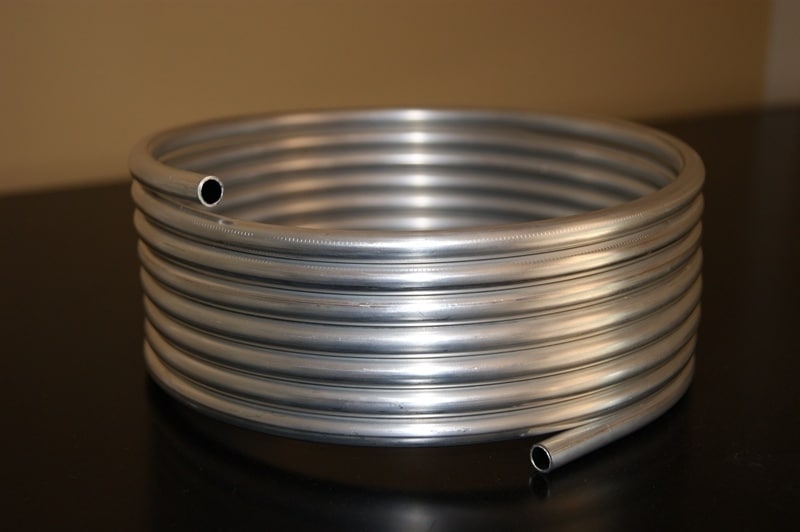
Aluminum finned tubes are a crucial component in various heat transfer applications, from industrial processes to HVAC systems. These specialized tubes are designed to enhance heat transfer efficiency by increasing the surface area available for heat exchange. In this article, we will delve into the world of aluminum finned tubes, discussing what they are, how they work, and their applications. We will also explore the advantages and disadvantages associated with using aluminum finned tubes in heat exchange systems.
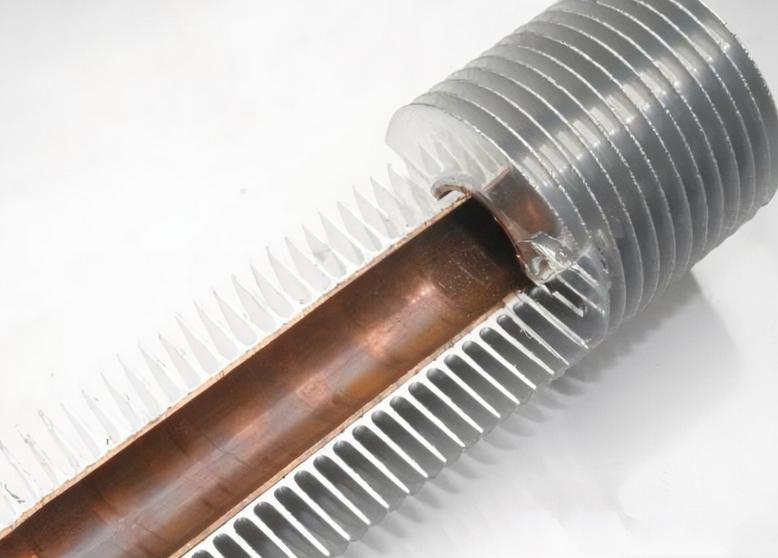

What are Aluminum Finned Tubes?
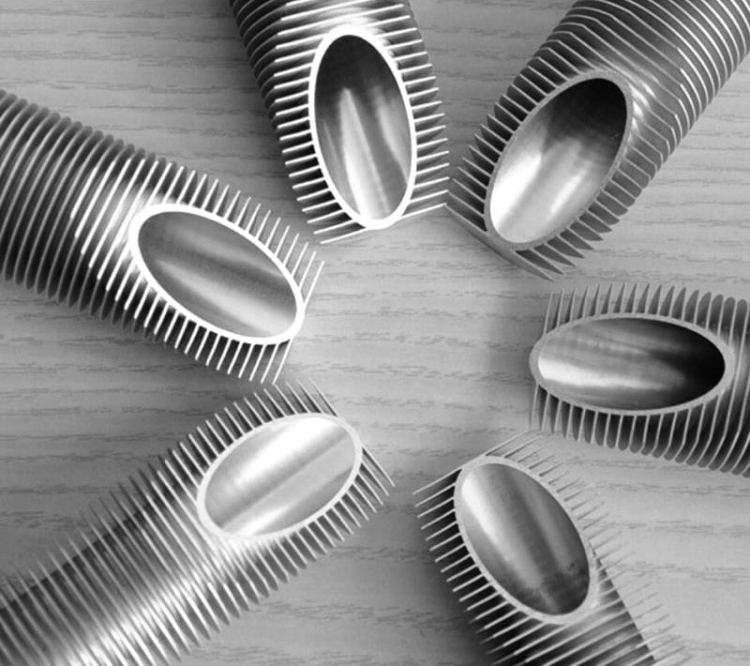
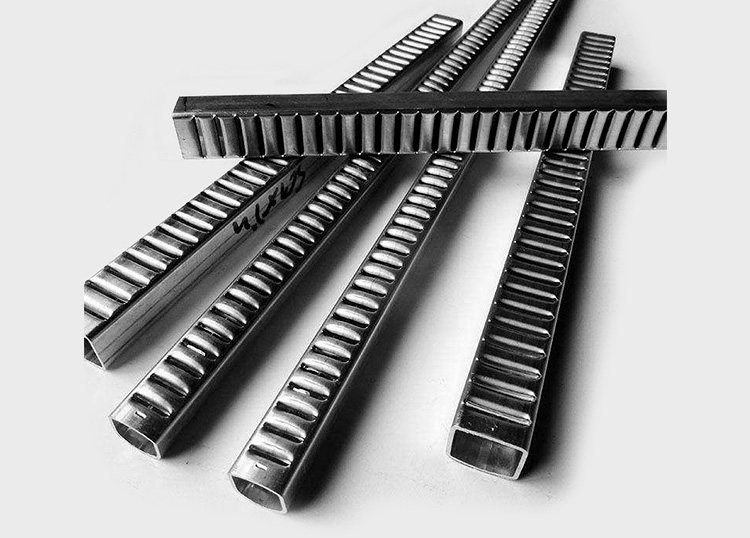
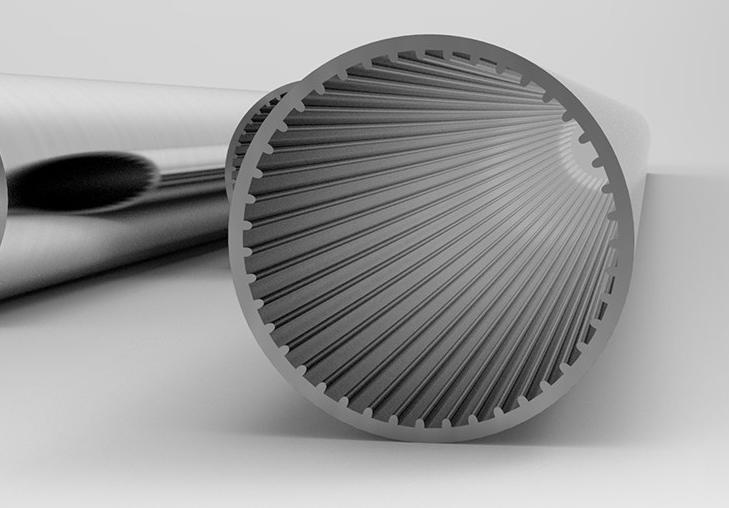
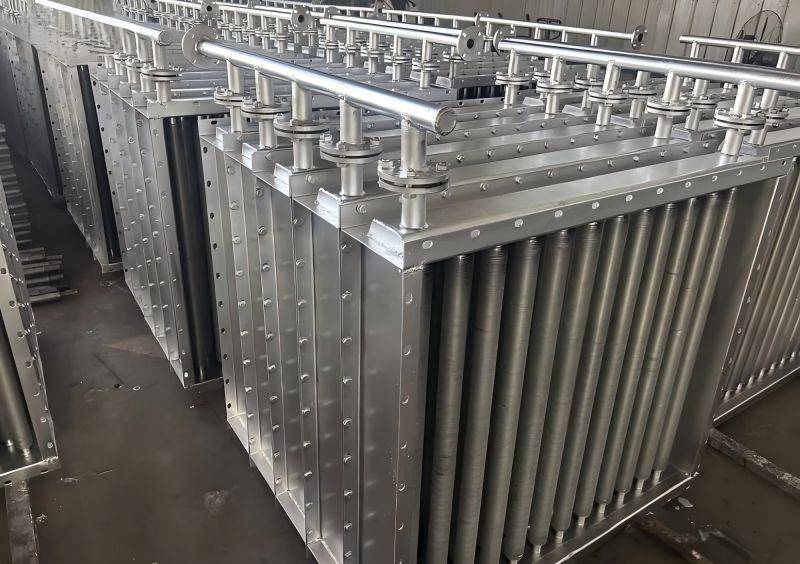
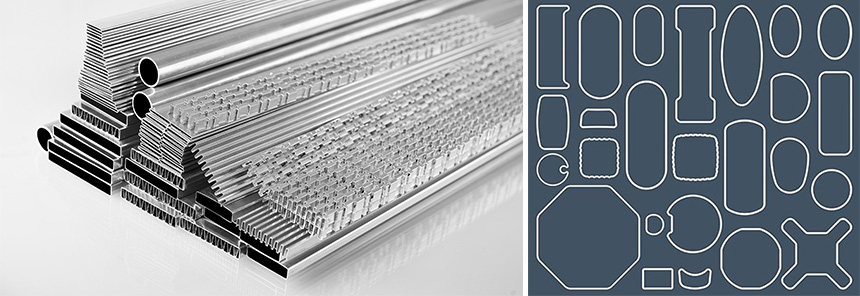
Aluminum finned tubes are heat exchanger components that consist of a base tube made of aluminum, with extended surfaces (fins) attached to the outer surface. The primary function of these fins is to increase the effective surface area for heat transfer, thus improving the overall efficiency of the heat exchanger. The fins are typically made of aluminum as well, but they can also be manufactured from other materials such as copper, steel, or stainless steel.
How Do Aluminum Finned Tubes Work?
The basic principle behind the functioning of aluminum finned tubes is to maximize the contact area between the fluid or gas being heated or cooled and the surrounding environment. The fins create an additional surface area, which allows for more efficient heat exchange between the medium inside the tube and the ambient air or another fluid outside the tube.
Aluminum is an excellent material for finned tubes because of its high thermal conductivity, which enables the efficient transfer of heat between the medium inside the tube and the fins. This enhanced heat transfer is vital for various applications where temperature control and energy efficiency are critical.
What are Aluminum Finned Tubes Used for?
Aluminum finned tubes are used in a wide range of applications across different industries. Some of the most common applications include:
- HVAC Systems: In heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, aluminum finned tubes are used in air-cooled condensers and evaporators. They help dissipate heat and ensure efficient cooling of refrigerants, making them an essential component for maintaining indoor comfort.
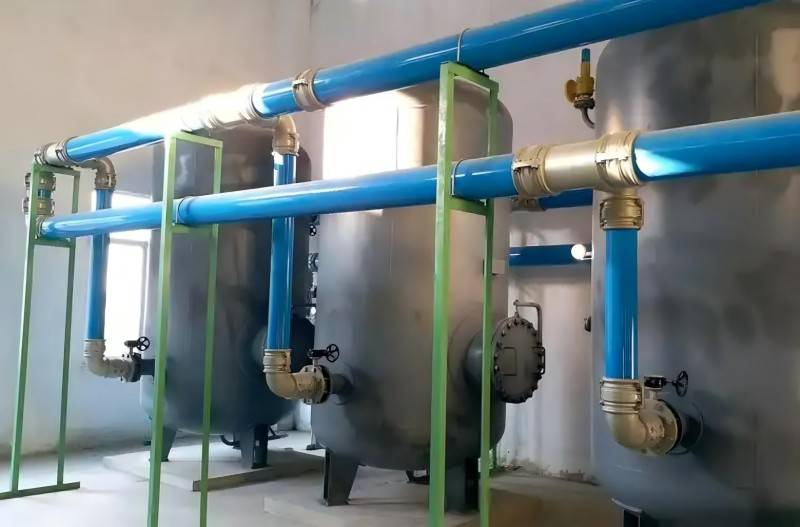
- Industrial Heat Exchangers: These tubes are widely used in various industrial processes, including power generation, chemical manufacturing, and food processing. They are employed in heat exchangers to facilitate heat transfer, ultimately improving process efficiency.
- Automotive Radiators: Aluminum finned tubes are also utilized in the automotive industry for the production of radiators, where they help manage engine temperatures by facilitating efficient heat dissipation.
- Oil and Gas Industry: In the oil and gas sector, aluminum finned tubes are employed in heat exchangers for processes such as natural gas liquefaction and refining, where precise temperature control is critical.

Advantages of Aluminum Finned Tubes
- High heat transfer efficiency: One of the most significant advantages of aluminum finned tubes is their high heat transfer efficiency. The increased surface area provided by the fins enables rapid heat exchange, making them ideal for applications where temperature control and energy efficiency are essential.
- Lightweight and easy to install: Aluminum is a lightweight material, making these tubes easy to transport, handle, and install. This can result in cost savings in terms of labor and installation time.
- Corrosion resistant: Aluminum is naturally corrosion resistant, which is a valuable trait for applications that involve exposure to moisture or corrosive substances. This resistance to corrosion ensures the longevity of the finned tubes, even in harsh environments.
- Ductile and malleable: Aluminum is a highly ductile and malleable material, allowing for the creation of intricate fin designs. This flexibility in design enables manufacturers to tailor the finned tubes to specific requirements and optimize their performance.
- Cost-effective: Aluminum is generally more cost-effective than materials like copper or stainless steel. This cost advantage makes aluminum finned tubes an attractive choice for applications where budget constraints are a concern.
Disadvantages of Aluminum Finned Tubes
- Lower thermal conductivity than copper: While aluminum has good thermal conductivity, it is not as efficient a conductor as copper. This means that, in some applications, copper-finned tubes may offer better heat transfer performance. It’s essential to consider the specific requirements of the application when choosing between the two materials.
- Softer and less durable than copper: Aluminum is softer and less durable than copper, making it more prone to damage, especially in high-impact or abrasive environments. Copper-finned tubes may have a longer lifespan in such conditions.
- Can be susceptible to galvanic corrosion when paired with other metals: Galvanic corrosion can occur when aluminum finned tubes are in contact with dissimilar metals in the presence of an electrolyte. Proper insulation and corrosion prevention measures are necessary to mitigate this risk.
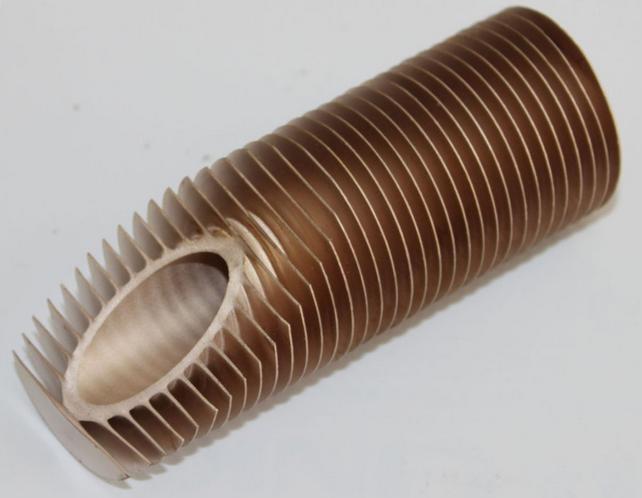

Conclusion
In summary, aluminum finned tubes are essential components in various heat transfer applications, offering numerous advantages and a few disadvantages. They excel in enhancing heat transfer efficiency, are lightweight and easy to install, corrosion-resistant, ductile, malleable, and cost-effective. However, they may have lower thermal conductivity than copper, be softer and less durable, and be susceptible to galvanic corrosion in certain situations.
Choosing the right material for finned tubes depends on the specific requirements of the application, including the desired heat transfer efficiency, environmental conditions, and budget constraints. By carefully considering these factors, engineers and designers can make informed decisions about whether aluminum finned tubes are the best choice for their heat exchange systems.