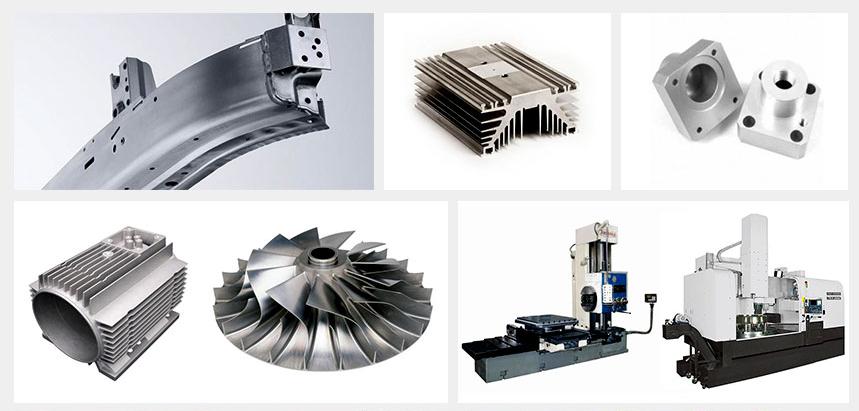
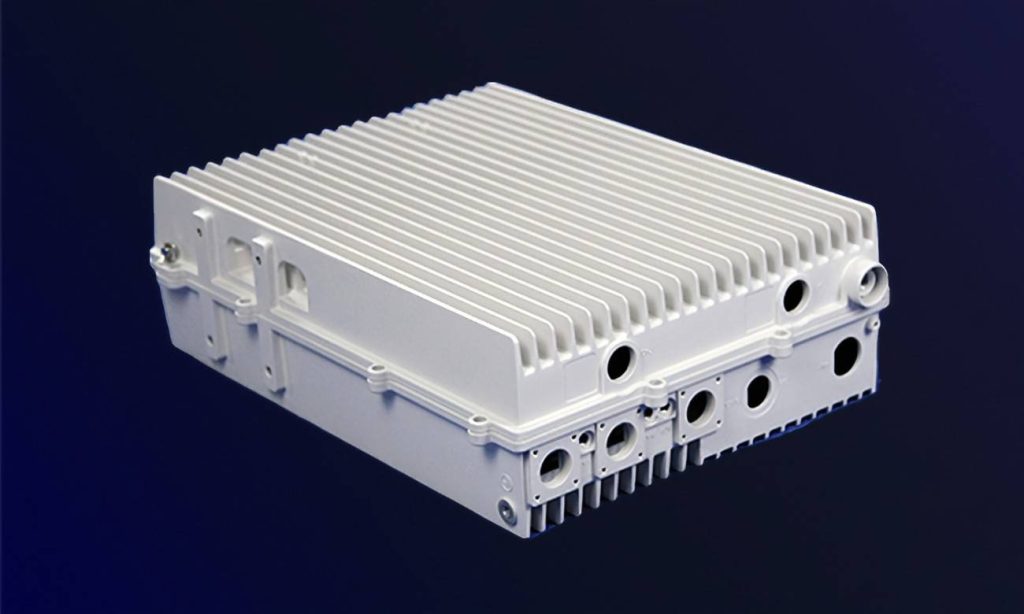
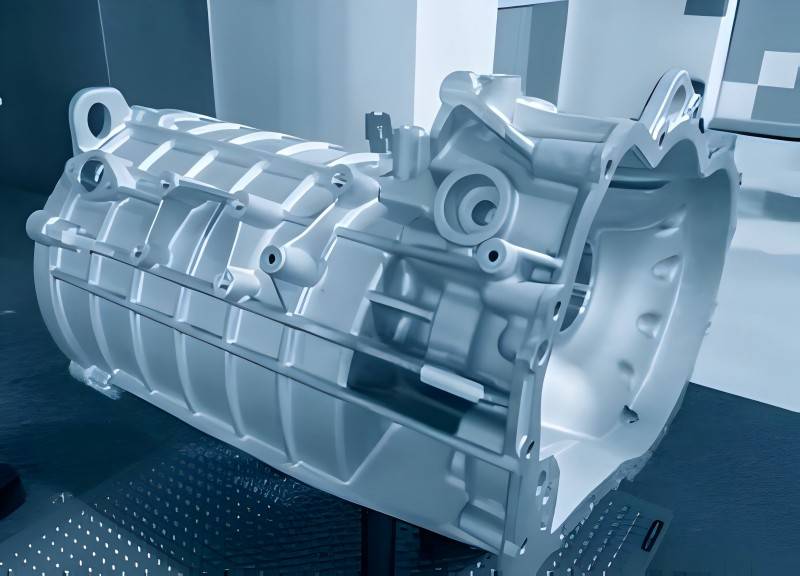
Aluminum motor housings have gained significant importance in various industries due to their excellent performance characteristics. The lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and thermally conductive properties of aluminum make it an ideal material for motor housings in a wide range of applications. In this article, we will explore the various application fields and manufacturing processes for aluminum motor housings in detail.
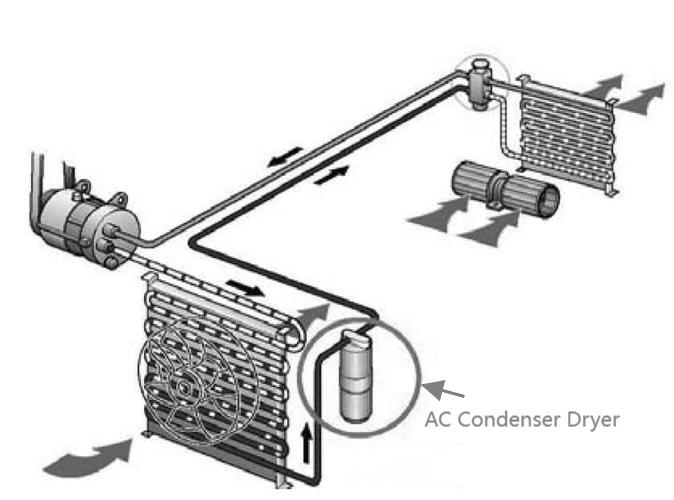
Applications of Aluminum Motor Housings
Aluminum motor housings have found widespread applications across industries that require durable, lightweight, and corrosion-resistant components. Some key fields include:
1. Electric Vehicles (EVs): In the rapidly expanding EV industry, the demand for lightweight materials is critical to extending vehicle range. Aluminum motor housings contribute to this by reducing overall weight without compromising structural integrity. The excellent thermal conductivity of aluminum also supports efficient heat dissipation, which is essential for electric motors that operate at high power levels. By maintaining optimal operating temperatures, aluminum housings help improve motor longevity and performance in electric vehicles.
2. Industrial Automation Equipment: Industrial automation often involves complex machinery such as CNC machines and robotics, where motor housings play a critical role in ensuring durability and performance. Aluminum motor housings provide superior electromagnetic shielding, which helps prevent interference from surrounding electronic devices. Additionally, the thermal conductivity of aluminum helps dissipate heat generated by high-performance motors, thus preventing overheating and maintaining equipment efficiency in demanding industrial environments.
3. Household Appliances: Household appliances like air conditioners, refrigerators, and washing machines are frequently subjected to moisture, dust, and varying temperatures. Aluminum motor housings enhance the durability of these appliances due to aluminum’s corrosion-resistant properties. Moreover, aluminum’s appearance lends a modern and aesthetic appeal, which is often preferred in consumer products. The use of aluminum also contributes to the lightweight design, reducing overall energy consumption and improving product efficiency.
4. Power Tools: Electric tools such as drills, saws, and grinders require motor housings that are both durable and lightweight to facilitate easy handling and maneuverability. Aluminum motor housings provide the necessary strength while keeping the tools lightweight, which is essential for user comfort and operational efficiency. Additionally, aluminum’s corrosion resistance and good thermal properties help power tools withstand challenging work environments, ensuring that they remain functional over prolonged use.
- Renewable Energy Equipment: Wind turbines and solar power systems, often located in harsh outdoor environments, benefit from aluminum motor housings due to their ability to withstand adverse weather conditions. These housings protect the motors from corrosion, rain, and UV exposure while ensuring optimal performance through efficient thermal management. In renewable energy applications, where maintenance may be challenging, aluminum’s durability and reliability are essential for the longevity and continuous operation of these systems.
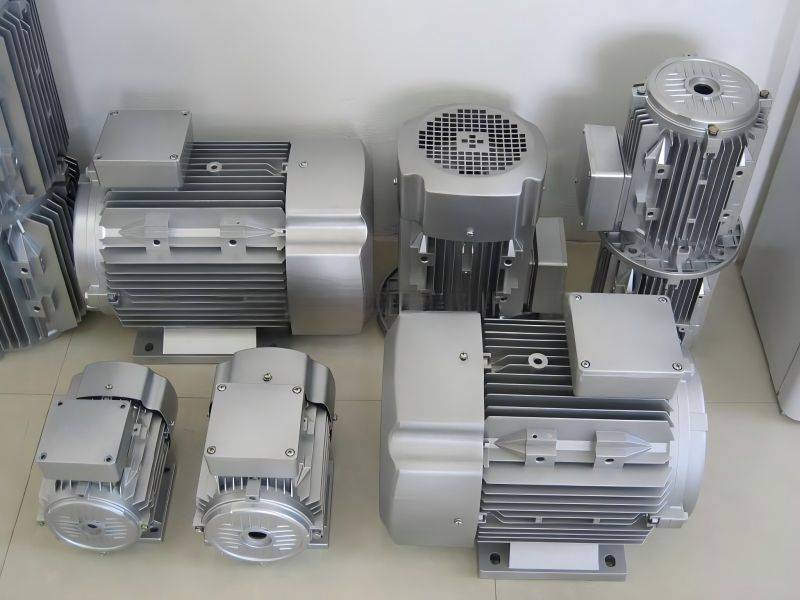

Manufacturing Processes for Aluminum Motor Housings
Common Aluminum Alloy Used for Aluminum Motor Housing
Choosing the appropriate aluminum alloy for motor housings is essential to ensure the desired mechanical and thermal properties. The most commonly used aluminum alloys include:
- 6061 Aluminum Alloy: Known for its balance of strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability, 6061 is widely used in general-purpose motor housings. It offers good durability and is easily processed in various manufacturing methods.
- 7075 Aluminum Alloy: This high-strength alloy is suitable for applications requiring high mechanical performance. Although it is slightly more challenging to work with than 6061, its superior strength and hardness make it ideal for motor housings that will be subject to significant stress.
- 5052 Aluminum Alloy: With excellent corrosion resistance, especially in marine or highly humid environments, 5052 is the preferred alloy for motor housings used in outdoor or harsh conditions. It is also highly formable, which makes it suitable for complex shapes.
4 Main Processes of Manufacturing Aluminum Motor Housings
Creating aluminum motor housings requires various manufacturing processes that accommodate different design requirements, performance standards, and economic considerations. Below are the primary manufacturing techniques used:
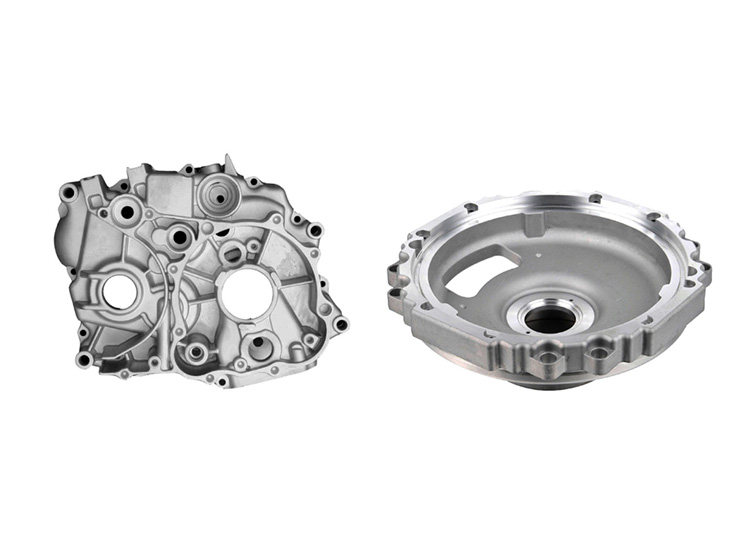
1. Die Casting
- Characteristics: Die casting is a high-efficiency process that allows for the creation of complex shapes in a single production step with excellent dimensional precision.
- Process: Molten aluminum alloy is injected into a mold under high pressure. Once the material cools and solidifies, the casting is removed from the mold.
- Applications: Die casting is suitable for motor housings with intricate shapes or uneven wall thicknesses, as it can achieve tight tolerances and high repeatability, making it ideal for mass production.
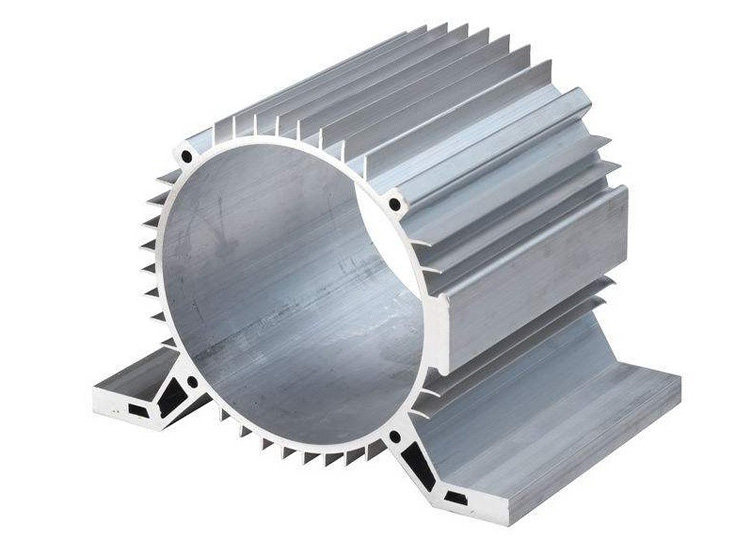
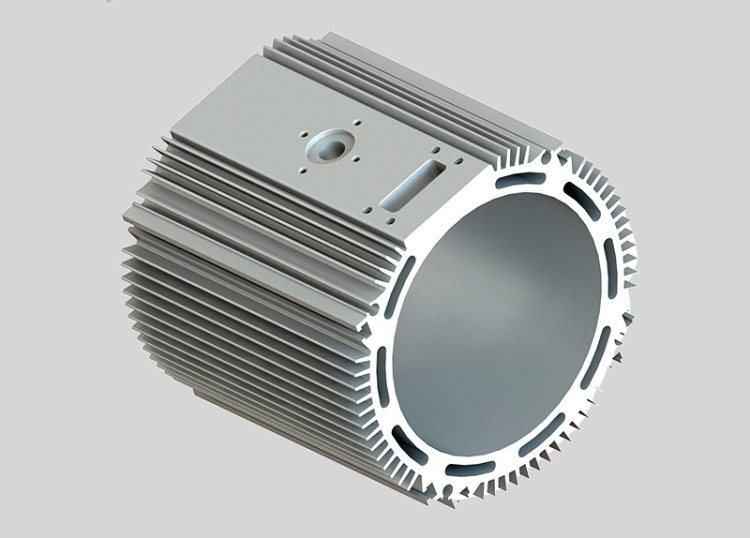
2. Extrusion
- Characteristics: Extrusion offers high material utilization, precision in dimensional tolerances, and a relatively low cost for simple shapes.
- Process: In extrusion, aluminum billets are heated and forced through a die to create long shapes with uniform cross-sections, such as tubes or bars.
- Applications: This process is used for producing motor housings with simpler, elongated shapes, typically with uniform thickness. Extrusion is often employed in applications requiring linear or tubular housing designs.
3. Forging
- Characteristics: Forging produces components with high density, excellent mechanical properties, and resistance to fatigue.
- Process: In the forging process, aluminum billets are heated and then deformed under high pressure using a hammer or press to achieve the desired shape and dimensions.
- Applications: This technique is ideal for motor housings that demand high strength and durability, especially in applications with significant mechanical stress.
4. Sheet Metal Fabrication
- Characteristics: Sheet metal fabrication is a flexible production method that allows for the customization of part shapes based on specific design requirements.
- Process: This process involves cutting, bending, and welding aluminum sheets to create motor housings. Techniques like laser cutting, CNC punching, and MIG/TIG welding are commonly used.
- Applications: Sheet metal fabrication is suited for housing designs with simple, box-like structures. It is often chosen for low-volume production or where custom designs are required.
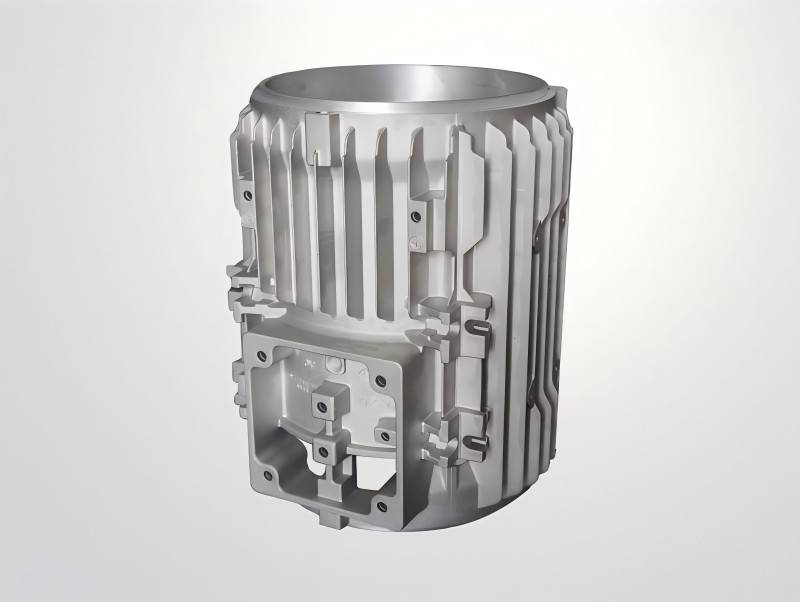

Common Surface Treatment for Aluminum Motor Housing
To improve corrosion resistance, aesthetics, and electromagnetic shielding, aluminum motor housings often undergo surface treatments. Common treatments include:
- Anodizing: Anodizing is an electrochemical process that enhances the natural oxide layer on aluminum, providing improved hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance. It is also available in various colors, which can enhance the visual appeal of motor housings.
- Electrophoretic Painting (E-Coating): This process deposits a thin layer of paint onto the aluminum surface, enhancing its corrosion resistance and improving appearance. E-coating is commonly used when uniform color and smoothness are desired.
- Powder Coating: Powder coating involves applying a dry powder to the aluminum surface and curing it under heat. This coating provides a durable, corrosion-resistant finish that also adds a decorative touch. Powder-coated housings are commonly used for outdoor applications where environmental exposure is a concern.
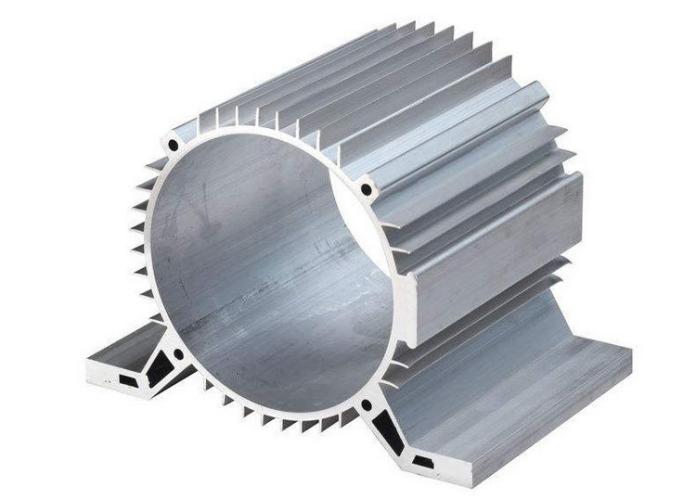

To sum up, aluminum motor housings are indispensable in a wide variety of industries due to their excellent properties. The manufacturing processes, such as die casting, extrusion, forging, and sheet metal processing, provide flexibility in creating motor housings tailored to specific needs. Choosing the right aluminum alloy and surface treatment further enhances the performance and durability of the motor housings. As demand for efficient and durable motor systems continues to rise, aluminum motor housings will remain a vital component in driving technological advancements across multiple sectors.