Aluminum paste, a crucial material in the electronics industry, has garnered significant attention due to its excellent conductivity, heat resistance, and cost-effectiveness. As a versatile conductive material, aluminum paste is employed in a myriad of applications ranging from solar cells to printed circuit boards (PCBs) and integrated circuits. The preparation technology of aluminum paste is a complex interplay of physics, chemistry, and materials engineering, encompassing various methods and processes that ensure its effectiveness in different electronic applications. This article explores the preparation technology of aluminum paste, the factors affecting its performance, its specific applications in electronics, and its inherent advantages and limitations.

Preparation Process of Aluminum Paste
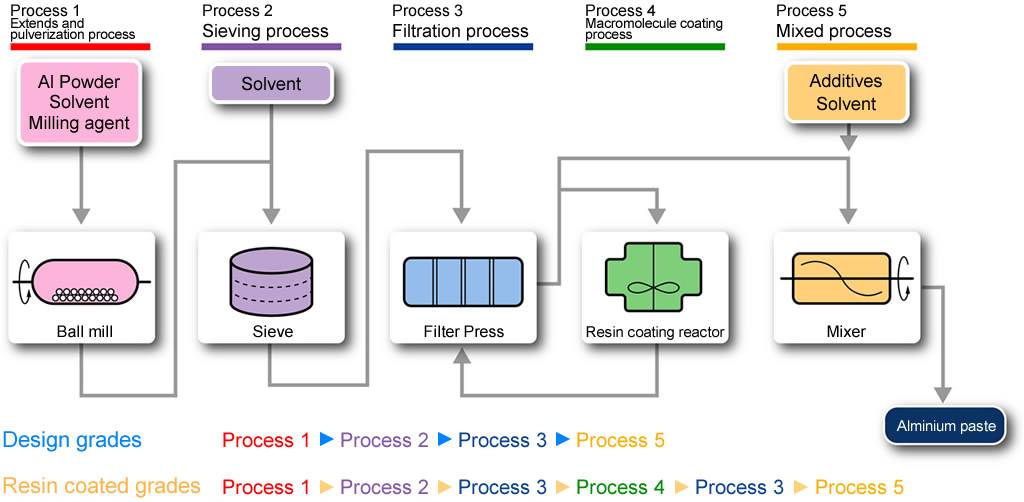
The preparation process of aluminum paste is a comprehensive technology involving physics, chemistry and materials engineering. Its preparation process mainly includes the following key steps:
1. Preparation of Aluminum Powder
The preparation of aluminum paste begins with the production of aluminum powder, which can be achieved through several methods:
- Mechanical Methods: These methods involve physically breaking down larger pieces of aluminum, such as blocks or sheets, into fine particles. Techniques like ball milling and grinding are commonly used to create micro- or nano-sized aluminum powders. Ball milling involves placing aluminum chunks in a rotating cylinder with milling balls, causing impact and friction that reduces the size of the aluminum particles. This method is favored for its ability to produce uniform particle sizes, which is crucial for achieving the desired properties in the final paste.
- Gas Phase Methods: This approach utilizes physical or chemical vapor deposition (PVD or CVD) to create aluminum powder. In this process, aluminum vapor is generated and subsequently condensed into fine particles upon cooling. The gas phase method is advantageous because it allows for greater control over particle size and morphology, leading to more consistent quality in the final aluminum powder.
2. Selection and Addition of Dispersants
Once the aluminum powder is prepared, the next crucial step is the selection and addition of dispersants. Dispersants play a pivotal role in enhancing the stability of the aluminum paste by preventing the aluminum particles from aggregating.
- Role of Dispersants: Dispersants work by adsorbing onto the surface of aluminum particles, effectively lowering their surface energy. This reduction in surface energy minimizes the tendency for particles to clump together, ensuring a stable suspension that can be processed further.
- Common Dispersants: Various types of dispersants can be utilized, including fatty acid salts, sulfonates, and phosphates. The choice of dispersant will influence the overall stability and performance of the aluminum paste. For instance, fatty acid salts are commonly used due to their effectiveness in stabilizing aluminum particles in solvent systems.
3. Mixing and Grinding
The mixing and grinding of aluminum powder and dispersants are essential to create a homogenous paste.
- Mixing Process: The aluminum powder and selected dispersants must be thoroughly mixed to ensure that the dispersants evenly coat the aluminum particles. This uniform distribution is vital for maintaining stability during storage and application.
- Grinding Techniques: Techniques such as ball milling and three-roll milling are employed to refine the particle size further and achieve a stable suspension. Ball milling involves the same principle as described earlier, while three-roll milling utilizes three rollers that rotate at different speeds to finely disperse the aluminum particles in the paste. The goal of this process is to achieve a smooth and homogenous paste that can be easily applied in various electronic applications.
4. Formulation of Paste
The formulation of aluminum paste involves several critical considerations that will determine its properties and suitability for specific applications.
- Selection of Solvents: The choice of solvent is paramount, as it affects the viscosity, stability, and flow characteristics of the aluminum paste. Common solvents include water, alcohol, and esters. Each solvent type brings unique properties that can influence the final paste’s performance.
- Adjustment of Solid Content: The concentration of aluminum powder in the paste must be tailored to meet specific application requirements. Increasing the solid content can enhance conductivity but may also increase viscosity, which could affect the application process. Striking the right balance is essential for optimizing performance.
- Addition of Additives: Depending on the intended application, various additives can be introduced to improve the properties of the aluminum paste. These may include binders to enhance adhesion, leveling agents to improve surface smoothness, and other functional additives tailored to specific performance requirements.
5. Stability Testing of the Paste
Once the aluminum paste is formulated, stability testing is conducted to ensure its performance in practical applications.
- Sedimentation Test: This test involves allowing the paste to sit undisturbed for a specified period and then observing for any sedimentation. A stable paste will show minimal sedimentation, indicating good dispersion of aluminum particles.
- Viscosity Measurement: The viscosity of the paste is measured to determine its suitability for printing or application. A paste with appropriate viscosity will flow easily without compromising the structural integrity of the printed patterns.
- Particle Size Distribution Measurement: The particle size distribution is assessed using instruments like laser particle size analyzers. Controlling particle size distribution is critical, as it affects the paste’s stability, conductivity, and overall performance.
Factors Affecting Aluminum Paste Performance
The performance of aluminum paste is influenced by several key factors:
- Particle Size and Morphology of Aluminum Powder: Finer aluminum particles have a larger surface area, enhancing dispersion and conductivity. However, excessively fine particles may lead to aggregation, which can adversely affect performance.
- Type and Amount of Dispersants: The selection and quantity of dispersants directly impact the paste’s stability. An insufficient amount may lead to poor dispersion, while excessive dispersant could negatively affect conductivity.
- Properties of Solvents: The polarity, viscosity, and evaporation rate of solvents will influence the flow characteristics and drying times of the paste, affecting application efficiency and performance.
- Mixing and Grinding Techniques: The thoroughness of mixing and the effectiveness of grinding methods significantly affect the uniformity and stability of the aluminum paste, impacting its overall performance.
Applications of Aluminum Paste in Electronic Devices
Aluminum paste is used extensively in various electronic applications, leveraging its unique properties to enhance performance and efficiency.
1. Solar Cells
- Back Electrode: In solar cells, the aluminum paste is used for back electrodes due to its high reflectivity, which enables effective light reflection back to the silicon substrate, improving photovoltaic efficiency.
- Front Electrode: Emerging solar cell technologies are exploring the potential of aluminum paste as a front electrode material, providing new avenues for innovation in solar energy capture.
2. Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs)
- Conductive Layers: Aluminum paste serves as a conductive layer in PCBs, facilitating connections between various electronic components.
- Shielding Layers: It is also employed in the creation of shielding layers to minimize electromagnetic interference, enhancing the overall performance of the electronic device.
3. Integrated Circuits
- Interconnects: Aluminum paste is utilized as a material for interconnects in integrated circuits, allowing for efficient connectivity and signal transmission between components.
4. Displays
- Electrodes: Aluminum paste is used to produce electrodes in liquid crystal displays (LCDs) and organic light-emitting diode (OLED) displays, playing a critical role in display functionality.
5. Other Electronic Components
- Capacitors: Some types of capacitors incorporate aluminum paste in their construction, benefiting from its conductive properties.
- Sensors: Specialized sensors also utilize aluminum paste, demonstrating its versatility across different electronic applications.

Advantages of Aluminum Paste
Aluminum paste presents several advantages that make it a preferred choice in various applications:
- Excellent Conductivity: Aluminum boasts a conductivity second only to silver, making it a cost-effective alternative with substantial conductive properties.
- High-Temperature Resistance: Aluminum’s high melting point allows it to maintain good conductivity even in elevated temperature environments, which is crucial for many electronic applications.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to silver paste, aluminum paste offers significant cost savings, making it an attractive option for manufacturers.
- Ease of Processing: Aluminum paste is easy to handle and process, facilitating efficient application techniques such as printing and coating.
Limitations of Aluminum Paste
Despite its advantages, aluminum paste also has limitations that need to be addressed:
- Oxidation Issues: Aluminum is prone to oxidation, which can negatively impact its conductivity. Protective measures must be implemented during processing and application to mitigate this issue.
- Decreased Mechanical Performance at High Temperatures: At extreme temperatures, the mechanical properties of aluminum can deteriorate, limiting its use in certain high-temperature applications.

Final Words
The preparation technology of aluminum paste is a multifaceted process that involves careful consideration of various factors affecting its performance. From the initial preparation of aluminum powder to the final formulation and testing of the paste, each step plays a crucial role in ensuring the effectiveness of aluminum paste in electronic applications. With its numerous advantages and growing range of applications, aluminum paste continues to be an essential material in the electronics industry, driving innovation and efficiency across various devices. Future advancements in preparation techniques and formulations may further enhance its performance, solidifying its place as a cornerstone in electronic manufacturing.