Aluminum pipe welding plays a vital role in numerous industries, from construction and aerospace to automotive and shipbuilding. While it offers distinct advantages due to aluminum’s lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties, welding this material presents unique challenges compared to steel. Understanding these challenges and implementing proper safety precautions are essential for protecting yourself and others from potential health hazards.
Health Risks Associated with Aluminum Welding
The welding process generates fumes containing hazardous airborne particles. Aluminum welding fumes pose a specific health risk due to the presence of metal oxides and ozone, a byproduct of the ultraviolet radiation emitted from the welding arc.
Aluminum Welding Fumes: Inhalation of these fumes can cause various acute health effects, including:
- Eye, nose, and throat irritation.
- Metal fume fever, characterized by flu-like symptoms such as chills, fever, and muscle aches.
Long-term exposure to aluminum welding fumes can lead to more severe health complications, including:
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), a progressive lung disease that makes breathing difficult.
- Asthma, a chronic inflammatory condition affecting the airways, leading to wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and coughing.
Radiation from the Welding Arc: The intense ultraviolet (UV) radiation emitted from the welding arc poses a significant threat to the eyes and skin.
- Eye damage can range from temporary flash burns (welder’s flash) to permanent vision loss, including cataracts.
- Skin burns can occur in exposed areas, similar to sunburn.
Essential Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) for Aluminum Welding
Utilizing the appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is the primary line of defense against the health hazards associated with aluminum welding.
1. Eye Protection
- Auto-darkening welding helmet: This helmet automatically adjusts the shade level of the visor based on the intensity of the welding arc. For aluminum welding, a shade level between 10 and 12 is typically recommended.
- Safety glasses: These are essential for protecting your eyes during grinding, cleaning, and other pre-welding activities. Ensure they comply with the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) Z87.1 standard for impact resistance.
2. Respiratory Protection
- Air-purifying respirator (APR): An APR equipped with appropriate cartridges specifically designed for aluminum welding fumes is crucial. These cartridges typically contain activated carbon and other filtration materials to absorb harmful contaminants.
- Proper fit and filter selection: Consult with a safety professional to ensure the selected respirator fits correctly and the filters provide adequate protection for the specific type of aluminum welding fumes encountered.
3. Skin and Body Protection
- Fire-resistant leather gloves and sleeves: These offer protection from heat, sparks, and spatter during the welding process.
- Flame-retardant clothing: Wear long pants and long-sleeved shirts made from flame-retardant materials like cotton or wool blend fabrics.
Workplace Safety Measures for Aluminum Pipe Welding
Creating a safe work environment for aluminum pipe welding goes beyond individual PPE. Effective workplace safety measures are critical for mitigating risks.
1. Ventilation
- Adequate ventilation: The most effective way to control welding fumes is to remove them at the source through a local exhaust ventilation (LEV) system. An LEV system captures fumes directly from the welding zone and removes them from the breathing zone of the welder and others in the vicinity.
- General ventilation: In addition to an LEV system, general ventilation throughout the workspace helps to dilute and remove any remaining airborne contaminants.
2. Fire Safety
- Fire extinguishers: Readily available and properly maintained fire extinguishers are essential for any welding operation. Ensure the type of fire extinguisher is suitable for potential fires involving flammable materials used in the welding process.
- Clean work area: Maintain a clean and organized work area free of flammable materials like solvents, rags, and welding waste. Regularly dispose of welding waste in designated containers.
Aluminum Material and Preparation for Safe Welding
The properties of aluminum itself significantly impact the welding process and safety considerations.
1. Understanding Aluminum Alloys
Different aluminum alloys are used in pipe applications, each with its own characteristics that affect weldability. A common alloy used in pipe welding is 6061, known for its good machinability and weldability. Knowing the specific alloy of the aluminum pipe is crucial for selecting the appropriate welding process and filler metal.
2. Cleaning Techniques for Aluminum
Aluminum readily forms a tenacious oxide layer on its surface. This oxide layer has a high melting point and hinders proper weld formation. Therefore, thoroughly cleaning the aluminum pipe before welding is essential. Chemical cleaning methods, such as solvent degreasers, can be used to remove oil, grease, and other surface contaminants. However, caution is advised, as some solvent degreasers can be flammable or hazardous if not handled properly. Always follow the manufacturer’s safety instructions when using solvent degreasers.
Brushing techniques are also commonly employed to remove the oxide layer. Brushing should be done with a stainless-steel brush in the direction of the weld to avoid contaminating the cleaned surface with debris. A dedicated brush used solely for aluminum cleaning is recommended to prevent cross-contamination with other metals.

Welding Process Considerations for Aluminum Pipes
The selection of the most suitable welding process for aluminum pipes depends on several factors, including the pipe thickness, joint configuration, and desired weld properties.
1. Welding Process Selection
- Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding: This process, also known as Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), is a popular choice for aluminum pipe welding due to its precise control and high-quality welds. TIG welding utilizes a non-consumable tungsten electrode and a separate filler metal rod to create the weld.
- Metal Inert Gas (MIG) welding: This process, also known as Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), is another option for aluminum pipe welding. MIG welding utilizes a continuously fed consumable electrode that also acts as the filler metal. While offering faster welding speeds compared to TIG, MIG welding can be more challenging to achieve high-quality welds on aluminum due to the potential for porosity (gas bubbles trapped in the weld metal).
2. Shielding Gas Selection
- Inert gas plays a critical role in protecting the molten weld pool from contamination by atmospheric gases like oxygen and nitrogen. These gases can cause porosity and weaken the weld.
- Argon is the most commonly used shielding gas for aluminum welding due to its inert properties. In some cases, a small amount of helium may be added to the argon to improve arc characteristics and travel speed.
Safe Work Practices During Aluminum Pipe Welding
Following safe work practices during the actual welding process is vital for minimizing health and safety risks.
- Proper Grounding Techniques: A secure electrical ground connection is essential for safety and weld quality. The ground clamp should be attached to clean, bare metal on the workpiece as close to the weld zone as possible.
- Electrode Selection and Handling: For TIG welding, select the appropriate tungsten electrode diameter and type based on the pipe thickness and desired weld characteristics. Handle the electrode carefully to avoid contamination of the tip, which can affect arc stability and weld quality. For MIG welding, ensure the selected filler metal is compatible with the specific aluminum alloy being welded.
- Arc Length and Travel Speed Control: Maintaining the proper arc length is crucial. A short arc length is recommended for aluminum welding to minimize the risk of porosity and achieve good weld penetration. Travel speed should be adjusted based on the material thickness and desired weld profile.
- Fire Watch Procedures: If welding is performed near combustible materials or in confined spaces, a fire watch is mandatory. A designated fire watcher should be positioned to monitor the welding area for potential fires and be equipped with a fire extinguisher to extinguish any flames immediately.
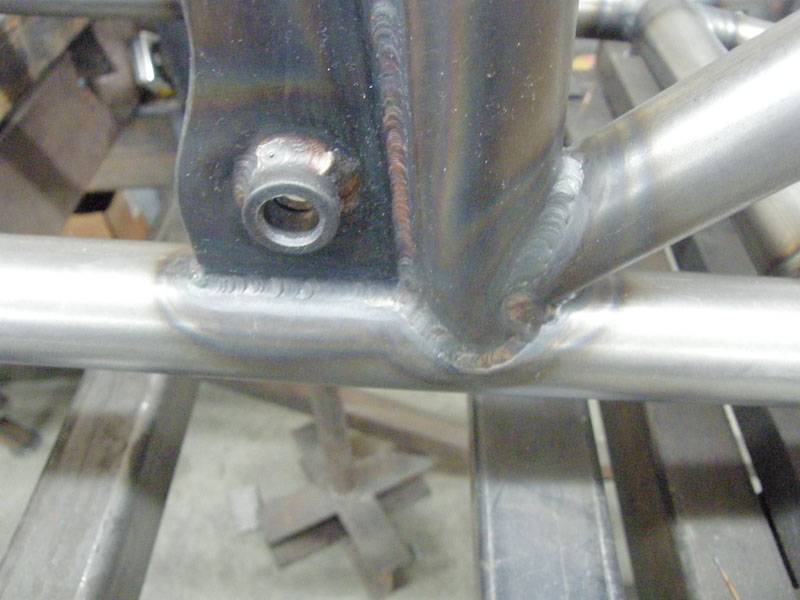

Conclusion
Aluminum pipe welding offers distinct advantages in various industries, but it necessitates prioritizing safety due to the associated health hazards. By understanding the potential risks, implementing appropriate personal protective equipment, and establishing effective workplace safety measures, welders can significantly reduce the likelihood of injuries and illnesses. Furthermore, proper selection of the welding process, filler metal, and shielding gas, coupled with safe work practices, ensures high-quality and reliable aluminum pipe welds.
For further information and more in-depth training on safe aluminum pipe welding procedures, it is highly recommended to consult with certified welding instructors and industry safety standards, such as those established by the American Welding Society (AWS).