Aluminum High-Frequency Welding (HFW) pipes are widely used in industries such as oil and gas, construction, and automotive due to their lightweight, corrosion resistance, and durability. However, manufacturing these pipes is not without challenges. From selecting appropriate materials to ensuring precision in the welding process, manufacturers face a range of common problems. Addressing these challenges is crucial to ensure the quality and reliability of the final product. Here we will discuss the most frequent problems encountered during the manufacturing of aluminum HFW pipes and provide practical solutions to address them.
Manufacturing high-quality aluminum HFW pipes requires careful control of various factors, including materials, processes, equipment, and quality checks, etc. Below, we detail four common problem areas and offer solutions to mitigate them.
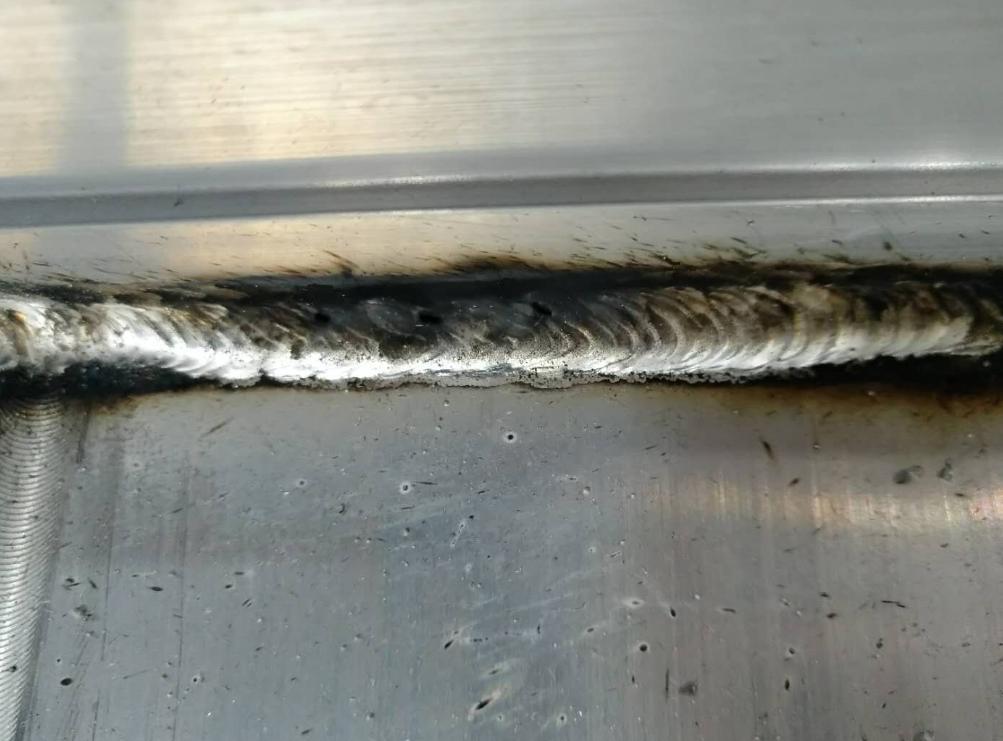

Problem 1: Material-Related Issues
The quality of the aluminum material used in HFW pipe manufacturing is crucial for producing pipes with desired properties. Impurities, defects, and improper alloy selection can lead to various problems.
- Oxidation: Aluminum has a natural tendency to form an oxide layer on its surface, which can interfere with the welding process.
- Inclusions: Impurities or foreign particles within the aluminum can weaken the weld area, resulting in poor bonding.
- Alloy inconsistencies: Variations in alloy composition can cause unpredictable weld behavior, leading to cracks or weak joints.
Solutions:
- Surface Preparation: Before welding, it is essential to thoroughly clean the aluminum to remove any oxide layer or contaminants. Using chemical treatments or mechanical cleaning methods can enhance weld quality.
- Material Selection: Choose high-quality, controlled-composition aluminum alloys that minimize inclusions and other defects.
- Pre-heating: In cases where alloy inconsistencies are problematic, pre-heating the aluminum can help ensure a more uniform weld and reduce the risk of cracking.
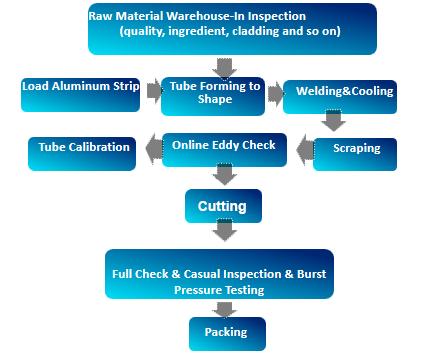
Problem 2: Process-Related Challenges
The HFW process involves several critical steps, including heating, forming, welding, and cooling. Issues related to these processes can result in defects, dimensional inaccuracies, and reduced efficiency.
- Incomplete Fusion: Occurs when the weld does not fully penetrate the material, leading to weak joints.
- Overlapping or Excess Material: This happens when too much material is added during welding, causing deformities in the pipe structure.
- Heat Affected Zone (HAZ) Issues: Improper heat distribution can result in uneven welds or changes in the aluminum’s mechanical properties.
Solutions:
- Optimize Welding Parameters: Fine-tuning the current, voltage, and welding speed can greatly improve the quality of the weld. Regularly monitor and adjust these parameters to ensure consistent results.
- Use Real-Time Monitoring: Implement real-time monitoring systems that measure temperature and weld penetration depth during the process. This ensures early detection of fusion issues or overheating.
- Post-Weld Heat Treatment: In some cases, post-weld heat treatment can help normalize the material properties in the heat-affected zone, improving the overall strength of the weld.

Problem 3: Equipment-Related Problems
The performance and reliability of the equipment used in HFW pipe manufacturing can significantly impact production efficiency and product quality. Issues such as machine wear, maintenance, and calibration can lead to defects and downtime.
- Wear and Tear on Welding Equipment: Over time, the welding electrodes or coils may degrade, leading to poor weld quality.
- Misalignment: If the welding equipment or the pipe itself is not properly aligned, it can result in uneven welds, affecting the structural integrity of the pipe.
- Inconsistent Power Supply: Fluctuations in the power supply can result in inconsistent welds, with sections of the pipe having weaker joints.
Solutions:
- Regular Maintenance: Ensure that all welding equipment is regularly maintained and replaced as needed. This includes checking for wear on electrodes and cleaning or replacing them when necessary.
- Proper Alignment: Use precision alignment tools to ensure that the pipe is correctly positioned in the welding machine. Misalignment can lead to defective welds and increased scrap rates.
- Stable Power Supply: Install voltage regulators or backup systems to ensure a stable power supply during the welding process. This reduces the risk of inconsistent welds caused by power fluctuations.
Problem 4: Quality Control Issues
Ensuring the quality of aluminum HFW pipes is essential for meeting customer requirements and maintaining a positive reputation. Quality control issues can arise at various stages of the manufacturing process, from material selection to final inspection.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) Failures: Sometimes, NDT methods such as ultrasonic testing or radiographic inspection may not detect all defects, leading to pipes with hidden flaws.
- Inconsistent Inspection Procedures: Variations in inspection techniques can result in some defects being overlooked.
- Lack of Data-Driven Feedback: Without data collection and analysis, it can be difficult to track recurring issues or make process improvements.
Solutions:
- Improve NDT Techniques: Ensure that advanced NDT techniques are employed, such as phased array ultrasonic testing (PAUT), which can detect deeper and more complex defects than standard methods.
- Standardize Inspection Protocols: Implement strict, standardized inspection procedures to reduce variability and ensure that all pipes are tested to the same level of scrutiny.
- Data Analysis and Feedback Loops: Collect and analyze data from the manufacturing process and inspection results to identify patterns of recurring problems. Use this data to implement process improvements and reduce defects.
Manufacturing aluminum HFW pipes is a complex process that involves various challenges related to materials, processes, equipment, and quality control. However, by addressing these common issues through improved material selection, optimized welding parameters, regular equipment maintenance, and stringent quality control measures, manufacturers can significantly enhance the quality of their products.