The selection of inner-grooved tubes is a critical decision in numerous industrial and everyday applications. Whether in refrigeration, heating systems, or heat dissipation for chemical and electronic equipment, the performance of inner-grooved tubes directly impacts the overall system efficiency, reliability, and cost. Copper and aluminum, as two common materials for inner-grooved tubes, each possess unique properties. Understanding these characteristics and the factors influencing inner-grooved tube performance is essential for making informed choices. This article delves into the properties of copper and aluminum inner-grooved tubes to assist readers in making wise decisions based on their specific application requirements.

What are Inner-Grooved Tubes?
Inner-grooved tubes are pipes with special grooves on their inner surface. These grooves are designed to enhance heat transfer efficiency or modify fluid flow characteristics within the tube. By increasing the contact area between the fluid and the tube wall and promoting turbulence, inner-grooved tubes significantly improve heat transfer rates. They are widely used in systems requiring efficient heat transfer or specific fluid flow control, such as evaporators and condensers in air conditioners and refrigerators, where inner-grooved tubes effectively transfer heat between different media.
Factors Affecting Inner-Grooved Tube Performance: Material Factors
The performance of inner-grooved tubes is influenced by several factors, including groove design, fluid dynamics, operating conditions, and, most importantly, material properties. While aspects like groove depth and pitch dictate the thermal and hydraulic performance, the material plays a pivotal role in determining the overall efficiency, durability, and cost-effectiveness of the tube.
From a material perspective, key factors include:
- Thermal Conductivity: A material’s thermal conductivity directly determines the tube’s heat transfer efficiency. Materials with high thermal conductivity can rapidly transfer heat from one side of the tube to the other, improving overall heat exchange.
- Corrosion Resistance: In many applications, inner-grooved tubes may be exposed to corrosive substances, such as acids or bases in chemical equipment. Poor corrosion resistance can lead to tube damage and affect system operation.
- Strength and Hardness: Inner-grooved tubes must possess sufficient strength and hardness to withstand internal fluid pressure and external mechanical stresses. Insufficient strength or hardness can cause deformation or rupture.
- Machinability: Good machinability enables the production of inner-grooved tubes with precise dimensions and shapes. This is crucial for ensuring the tube’s performance and compatibility with other components.
Understanding these material-specific factors is crucial for selecting the right tube for your application. Then let’s get to know the properties of these two materials.
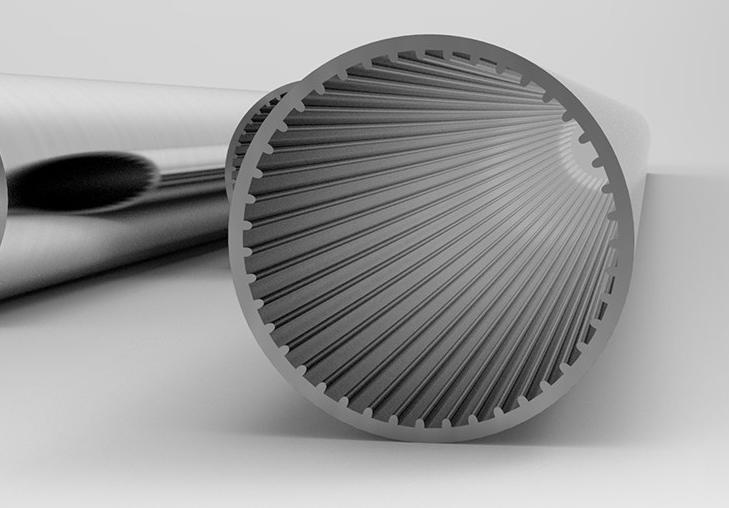

Properties of Copper Inner-Grooved Tubes and Aluminum Inner-Grooved Tubes
Copper and aluminum are the two primary materials used, each offering distinct advantages and challenges. The table provides a clear comparison of these two material:
| Property | Copper Inner-Grooved Tube | Aluminum Inner-Grooved Tube |
| Thermal Conductivity | Very high, making it an excellent heat conductor. Ideal for applications requiring high heat transfer rates, such as condensers in high-end refrigeration systems. | Good thermal conductivity, suitable for applications with moderate heat transfer requirements. Cost-effective compared to copper. |
| Corrosion Resistance | Relatively good, especially in non-oxidizing environments. Can be improved with surface treatments for specific corrosive environments. | Forms a natural oxide layer for some corrosion resistance. However, susceptible to corrosion in acidic or alkaline environments. |
| Strength and Hardness | Relatively high, capable of withstanding higher pressures and mechanical stresses. Suitable for applications with high pressure requirements, such as high-pressure pipelines in large air conditioning systems. | Relatively lower strength and hardness, but can be improved through alloying. Suitable for applications with lower pressure requirements, such as evaporators in small household refrigeration systems. |
| Machinability | Excellent machinability, allowing for the production of complex shapes. Can be manufactured with precise inner groove structures through processes like extrusion. | Good machinability. Requires careful control of processing parameters to ensure dimensional accuracy due to its softer nature. |
Understanding these material properties helps in aligning the tube selection with the specific demands of your application. While copper excels in performance and durability, aluminum provides an economical and lightweight alternative. Choosing the right material requires balancing these factors against your project’s requirements and constraints.

Key Factors to Consider When Choosing
When choosing copper or aluminum inner groove tubes, in addition to the characteristics of the material itself, you need to consider a variety of factors to ensure the rationality of material selection. Here are some key considerations:
Heat Transfer Efficiency Requirements
If the application demands extremely high heat transfer efficiency, such as in large industrial refrigeration equipment or high-performance electronic cooling systems, copper inner-grooved tubes might be the better choice. Their high thermal conductivity ensures rapid heat transfer, improving overall system performance. However, if the heat transfer efficiency requirements are not very stringent, aluminum inner-grooved tubes can be a viable option due to their cost advantages.
Operating Environment
- Corrosive Environments: If the inner-grooved tube will be used in a corrosive environment, such as in chemical equipment, the choice should be based on the specific corrosive medium. Copper tubes may be more suitable in less oxidizing environments without strong acids or bases, while aluminum tubes can be used in some acidic or alkaline environments with appropriate protective measures.
- Temperature and Pressure Environments: In high-temperature and high-pressure environments, copper tubes, with their higher strength and excellent thermal conductivity, may have an advantage. In low-temperature and low-pressure environments, aluminum tubes can be a more cost-effective option if they meet the strength requirements.
Cost Factors
The raw material cost of aluminum is relatively low, and the processing costs can also be relatively lower. If the budget is limited and the application allows, aluminum inner-grooved tubes are a more economical choice. However, if performance is a higher priority and cost is not the primary consideration, the high performance of copper tubes is more worth choosing.
System Compatibility
Inner-grooved tubes need to be compatible with other components in the system. For example, in some electronic devices, special connection measures may be required due to the possibility of electrochemical corrosion when copper is connected to other metals. When connecting aluminum inner-grooved tubes with certain plastic components, issues such as sealing and thermal expansion coefficient matching may need to be considered.
When choosing copper or aluminum inner groove tubes, you need to consider multiple factors such as heat transfer efficiency, use environment, cost and system compatibility. No material is the absolute best choice. Only by weighing various factors according to specific application scenarios can you make the best decision. It is recommended to fully communicate with professional engineers or technicians before making a choice to obtain more professional advice.