With the increasing popularity of electric vehicles, people are paying more and more attention to the various components of electric vehicles and their working principles. In traditional fuel vehicles, the radiator is a very important component used to cool key components such as the engine. So, do electric vehicles also have radiators? This is a question that many people are concerned about. Electric vehicles are mainly powered by batteries. Although there is no traditional fuel engine, the batteries, motors, and other components of electric vehicles will also generate heat during operation. If this heat cannot be dissipated in time, it will affect the performance, safety, and service life of the electric vehicle. So electric cars do have radiators.
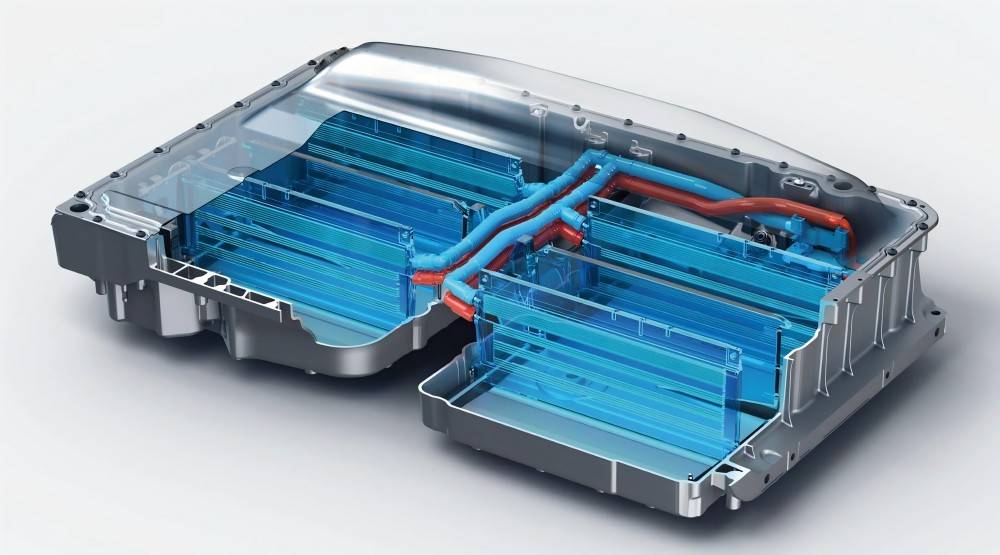
Types of Electric Vehicle Radiators
Due to their unique power system structure, electric vehicles have different types of radiators from traditional fuel vehicles. These radiators dissipate heat for different heat-generating components of electric vehicles.
Battery Pack Thermal Management System (BTMS)
Batteries are the core components of electric vehicles, and batteries generate heat during charging and discharging. The main task of the battery pack thermal management system is to maintain the optimal operating temperature of the battery:
- When the temperature is high, it needs to dissipate heat effectively to prevent accidents such as thermal runaway that seriously endanger safety;
- When the temperature is low, it needs to preheat the battery, increase the battery temperature, and ensure the charging and discharging performance and safety of the battery in a low temperature environment;
- At the same time, it needs to reduce the temperature difference within the battery pack, inhibit the formation of local hot zones, and prevent the battery from decaying too quickly at high temperature locations, thereby reducing the overall life of the battery pack.
Common heat dissipation methods include immersing the battery cells or modules in insulating liquids (such as mineral oil), or setting cooling channels between battery modules, or using cooling plates at the bottom of the battery.
Drive Motor Cooling System
The drive motor of an electric vehicle will also heat up during operation. The heat dissipation of the drive motor of a pure electric vehicle usually adopts liquid cooling, which is equipped with a cooling fan, a water tank radiator and a cooling water pump, and the motor heats up through the circulation of coolant. Cooling fans are divided into intelligent temperature-controlled fans and non-temperature-controlled fans. For better performance and energy efficiency, it is recommended to use a DC brushless fan, which does not require an electronic cooling fan for the ECU. When selecting the fan, you should also pay attention to the fan’s diameter, speed, temperature resistance, protection level, air exchange method and other parameters.
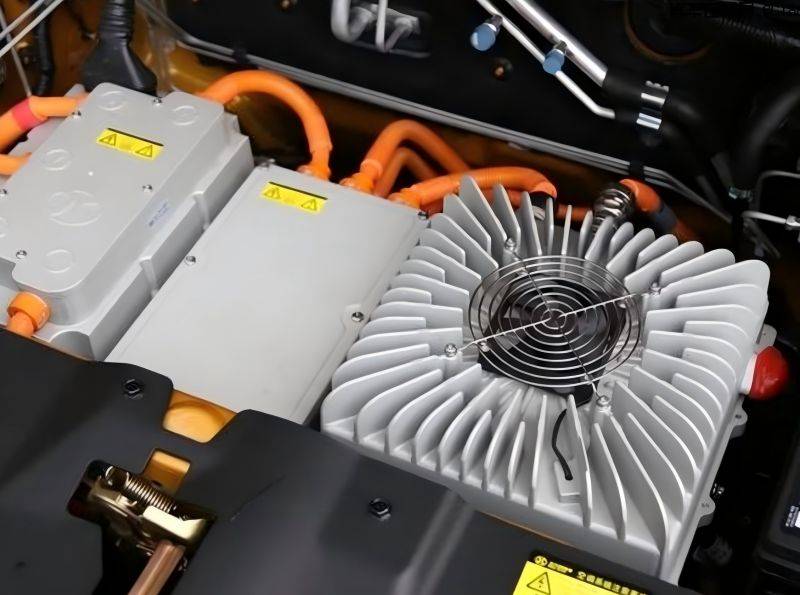

Heat Dissipation of Other Components
For example, IGBT modules (key components in power components for electric vehicles) have high heat generation. The quality of heat dissipation directly affects the reliability of the entire vehicle. Liquid cooling is often used, such as pin-fin water-cooled radiators.
There are various types of radiators for electric vehicles. Different heat dissipation methods are used for different key components such as batteries, motors and power components. These radiators jointly ensure the normal working temperature of various components of electric vehicles.
Radiator Materials and Design
The material and design of the radiator are the key factors that determine its heat dissipation efficiency. In the cooling system of electric vehicles, aluminum materials are widely used due to their many excellent properties. Different types and grades of aluminum materials play a unique role in various heat dissipation components.
Types and Grades of Aluminum Materials Used in Radiators
3003 Aluminum Plate
This is a common aluminum-manganese alloy that is widely used in electric vehicle radiators. 3003 aluminum plate has good forming and processing properties and can be easily processed into various shapes required for radiators, such as flat water pipes and heat sinks with corrugated fins. It also has good corrosion resistance, can maintain stable performance in complex working environments, and extend the service life of the radiator. In addition, it has moderate strength, which is sufficient to meet the structural requirements of the radiator under normal working conditions.
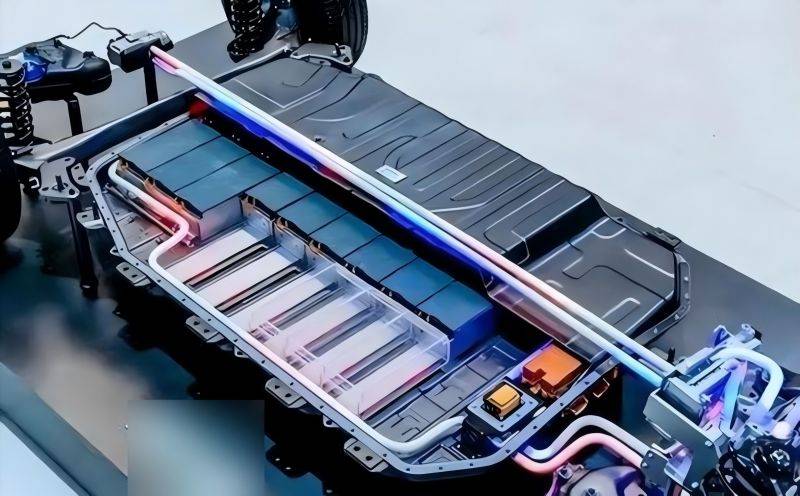

3003 + 4045 Brazing Plate
This composite plate is composed of 3003 aluminum alloy and 4045 aluminum alloy. 3003 aluminum alloy provides basic properties such as good forming processing performance and corrosion resistance, while 4045 aluminum alloy plays an important role in the brazing process. As a brazing filler material, 4045 aluminum alloy has good fluidity and wettability, which can ensure good bonding during the brazing process. This composite plate is widely used in heat dissipation components such as water cooling plates of electric vehicles, which helps to improve the overall thermal conductivity of the heat dissipation system.
Heat-free Aluminum Alloy (such as the product independently developed by Changchun Longda, a subsidiary of Lizhong Group)
This new type of heat-free aluminum alloy has also begun to emerge in the manufacture of electric vehicle radiators. It can effectively improve the lightweight level of electric vehicles, thereby improving the performance and energy efficiency of electric vehicles. In the manufacture of radiators, it not only retains the good thermal conductivity of aluminum materials but also simplifies the production process and reduces production costs through the characteristics of heat-free treatment.
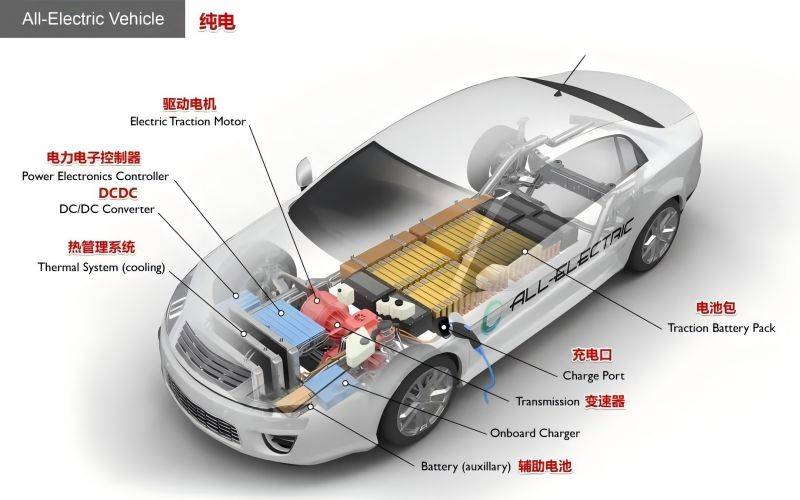
Combination of Aluminum Materials and Radiator Design
In addition to the characteristics of aluminum materials themselves, its close combination with the design of radiators is also the key to improving heat dissipation efficiency. For example, in the design of some radiators, aluminum water pipes adopt a planar structure and are equipped with corrugated fins between adjacent cooling pipes. This design takes advantage of the good plasticity of aluminum materials and improves the heat dissipation effect by increasing the heat dissipation area. For example, in the design of some integrated radiators, aluminum materials are used to manufacture heat dissipation cores with different functions, such as engine heat dissipation cores, motor heat dissipation cores, etc. Through reasonable layout and structural design, these aluminum heat dissipation cores can effectively reduce the volume and space occupancy while ensuring ventilation and heat dissipation, reduce the overall weight, and facilitate assembly in the limited space of electric vehicles.
Aluminum materials have an irreplaceable position in the material selection of electric vehicle radiators. Different types and grades of aluminum materials are combined with ingenious designs to provide efficient, reliable and lightweight solutions for electric vehicle cooling systems.
In general, although electric vehicles do not have traditional fuel engines, they also need radiators because key components such as batteries and motors generate heat during operation. These radiators are an important part of ensuring the performance, safety and service life of electric vehicles. With the continuous development of electric vehicle technology, radiator technology will also continue to improve to meet higher heat dissipation requirements.