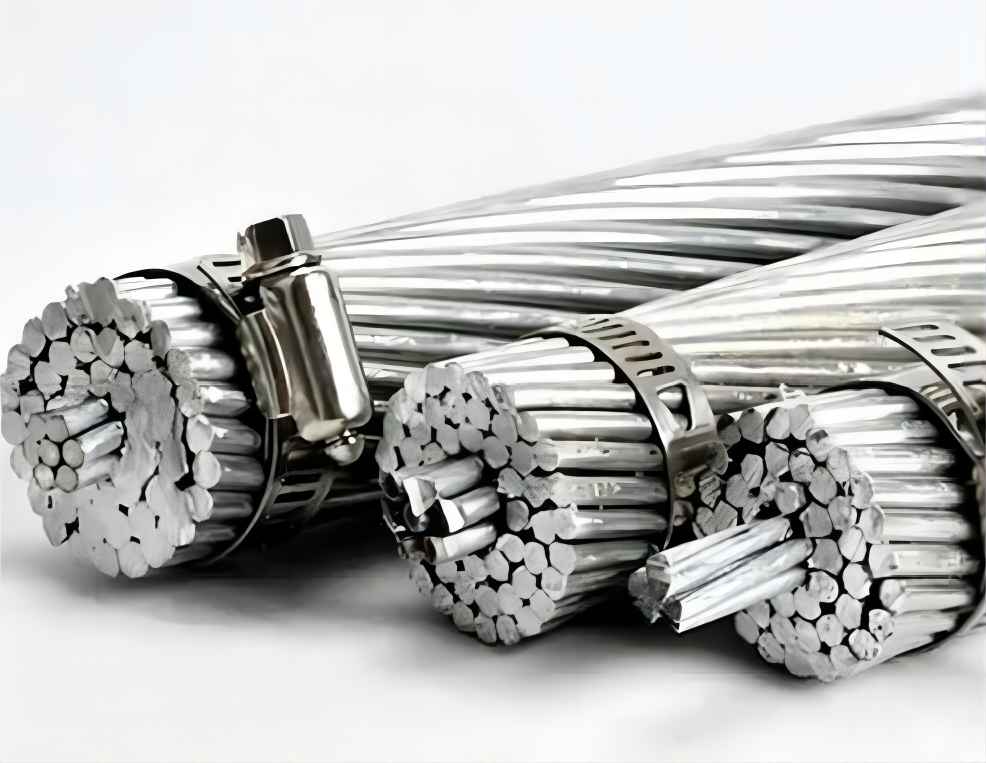
Aluminum wire is a wire that is used for electrical wiring in houses, power grids and airplanes. When compared to copper wire, aluminum wire is a more affordable solution considering its electrical and mechanical characteristics. Due to its inferior electrical conductivity versus copper, aluminum is rarely employed in tiny applications like residential wiring. Aluminum wire, however, became a popular option in the 1960s when copper prices surged.
What is Aluminum Wire?
Aluminum wire refers to its entire longitudinal length, and a uniform cross-section refers to a metal wire-shaped material made of pure aluminum or aluminum alloy. Aluminum wire is a core-pressed product and is created in coils. The cross-sectional shapes are circle, ellipse, square, rectangle, equilateral triangle and regular polygon, etc. The material is divided into pure aluminum wire and alloy aluminum wire. But according to the function, there are industrial aluminum wire and process aluminum wire.
These are common specifications and models: 1050, 1060, 1070, 1100, 2011, 2017, 2A16, 2A02, 2024, 3003, 3005, 3A21, 4A01, 5003, 5005, 5052, 5056, 5083, 6061, 6063, 6065, 7003, 7005, 7050, 7075, 8011, etc.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Aluminum Wire
Advantages
- Cheaper price
The price of pure copper wire is several times more expensive than pure aluminum wire, and copper is several times heavier than aluminum. In general, the per meter price of aluminum will be much cheaper than copper in the market. And it is more appropriate for low-cost projects or some temporary electricity.
- Light aluminum cable wire
Since metal aluminum is much lighter than metal copper, the weight of aluminum cable wire per square meter accounts for about 40% of copper cable. In terms of transportation costs, aluminum wire is also much cheaper than copper wire.
- Oxidation and corrosion resistance
The chemical properties of aluminum are very special. After long-term contact with the air, a chemical reaction will occur, forming an oxide film on the surface, which can effectively prevent further oxidation. Therefore, aluminum wire is better than other materials for high-voltage, large-section, and long-span overhead transmission, but these advantages in low-voltage lines no longer exist.

Disadvantages
Aluminum wire has low electrical conductivity, large electrical loss, poor tensile strength, and low corrosion resistance, and the joint part is particularly easy to oxidize. If it connects with copper wire, the joint part is more likely to corrode due to the potential difference, and it is easy to cause circuit breakage.
Connection of Aluminum Wire
Because the aluminum wire is easy to be oxidized and the resistivity of the oxide film is high, the connection method of the copper wire is not suitable for the aluminum core wire. Aluminum conductors shall be crimped with bolts and crimped with tubes. The bolt crimping method is suitable for the connection of aluminum core wires with small loads. The crimping tube crimping method is suitable for the connection of multi-strand aluminum conductors with large loads (also applicable to copper conductors). When crimping, choose a suitable aluminum crimping tube according to the specifications of the aluminum core wire. Clean the crimping place first, insert the two aluminum core wires into the crimping tube relative to each other, so that the two wire ends extend out of the crimping tube by about 30mm, and then crimp with the crimping pliers. When crimping, the first pressure pit should be pressed on one side of the end of the aluminum core. The crimping quality should meet the technical requirements.
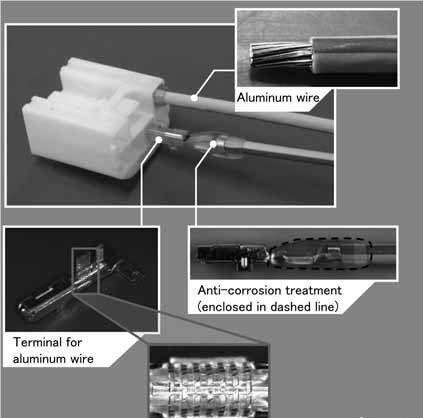
Will Aluminum Wire Replace Copper Wire?
Aluminum wire is mainly used for overhead power lines and automotive battery cables, where the conductors have a large cross-sectional area to support large currents. However, the conductor cross-sectional area of the wire harness usually does not exceed 2.5 mm2. To this end, many companies have developed small diameter aluminum wire harnesses for this type of automotive application.

As CO2 emissions regulations become more stringent, the demand for lightweight wiring harnesses is also increasing, and the need for weight reduction is also increasing. In addition, due in part to the skyrocketing price of copper, significant weight savings can be expected by replacing traditional copper wires with aluminum wires. However, the aluminum wire has the disadvantages of low electrical conductivity, low tensile strength, poor work-ability, strong surface insulating oxide film, and galvanic corrosion. Anyway, the technology of aluminum wire is becoming more and more mature, and the application of aluminum wire is increasing. There is a lot of momentum to replace copper conductors, but it will certainly be a long process.

















