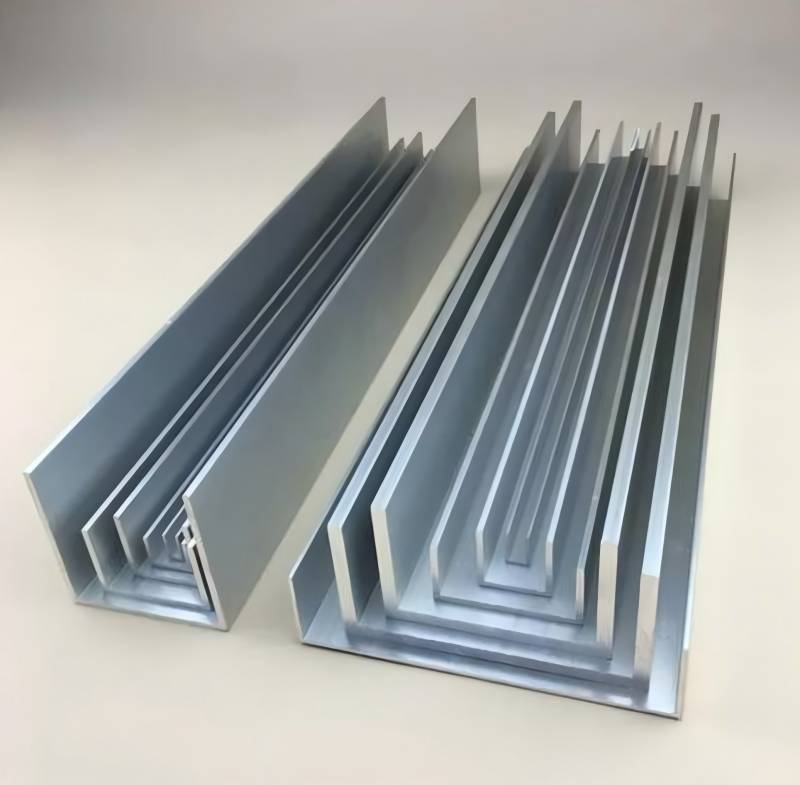
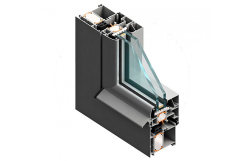
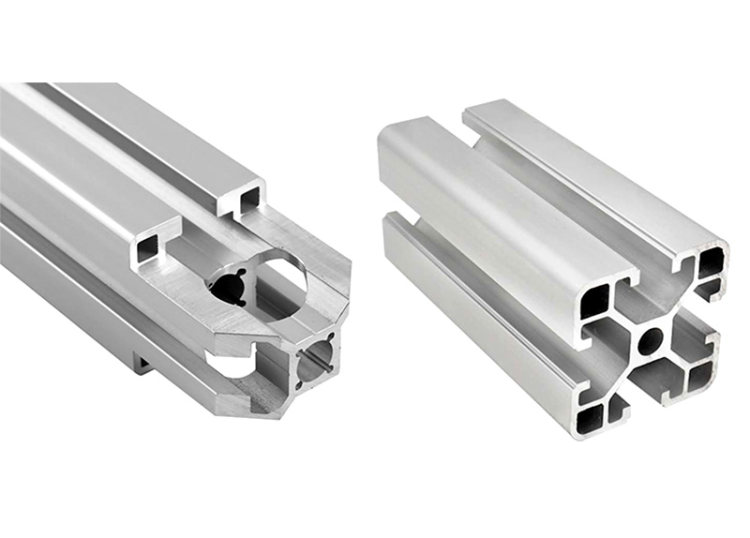
Aluminium extrusion profiles have become ubiquitous in modern construction, manufacturing, and everyday life. Their versatility, lightweight nature, and excellent mechanical properties make them a preferred choice for a wide range of applications. This article delves into the key aspects of these profiles, covering their types, dimensional considerations, recycling practices, and the diverse range of aluminium alloys used in extrusion processes.

What is Aluminium Extrusion?
Aluminium extrusion is a manufacturing process where aluminium is heated and forced through a shaped die to create long, continuous profiles with precise cross-sections. These profiles can range from simple shapes like angles and channels to complex, customized geometries designed for specific applications. The resulting extrusions offer numerous advantages, including:
- High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Aluminium is a lightweight yet strong metal, making it ideal for applications where weight reduction is crucial.
- Versatility: The extrusion process allows for the creation of a vast array of shapes and sizes, catering to diverse design requirements.
- Excellent Corrosion Resistance: Aluminium naturally forms a protective oxide layer, enhancing its resistance to corrosion and weathering.
- Good Thermal and Electrical Conductivity: These properties make aluminium extrusions suitable for various thermal and electrical applications.
- Sustainability: Aluminium is highly recyclable, making it an environmentally friendly material choice.
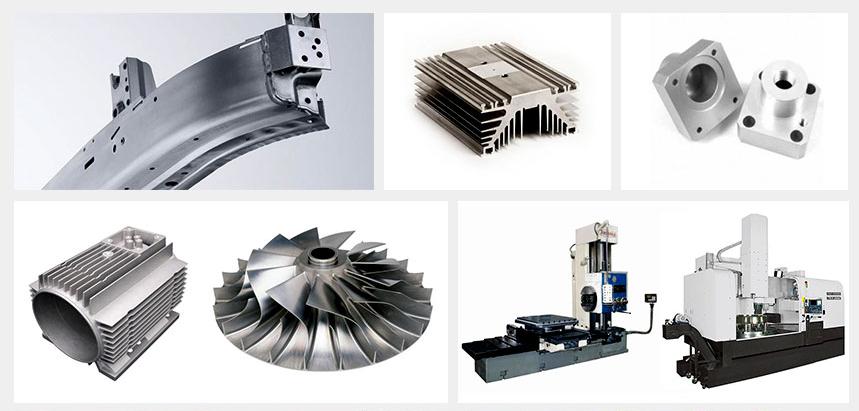
What are theTypes of Aluminium Extrusion Profiles?
Aluminium extrusion profiles can be classified based on their shape or their intended application:
1. Shape-Based Classification
Standard Shapes: These are commonly available profiles with standardized cross-sections, offering convenience and cost-effectiveness. Examples include:
- Angles: Used for structural support, framing, and corner reinforcement.
- Channels: Employed in framing, structural support, and as guide rails.
- I-Beams: Widely used in construction for beams and columns due to their high strength-to-weight ratio.
- Square Tubes: Versatile profiles used in various applications, including furniture, enclosures, and structural framing.
- Round Tubes: Commonly used in handrails, railings, and decorative elements.
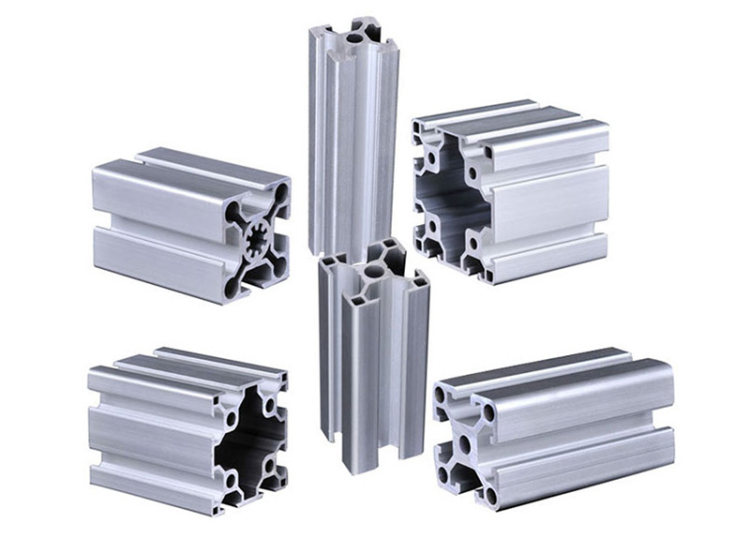
Custom Shapes: These profiles are designed and manufactured to meet specific customer requirements, offering greater design flexibility. Custom shapes can incorporate intricate features, such as:
- Internal channels: For housing wires, cables, or fluids.
- Reinforcements: For increased strength in critical areas.
- Special contours: To achieve specific aesthetic or functional requirements.
2. Application-Based Classification
Architectural Profiles: Used extensively in building and construction, including:
- Windows and Doors: Frames, sashes, and hardware components.
- Curtain Walls: Structural components and decorative elements.
- Facades: Cladding systems and architectural accents.
Industrial Profiles: Used in various industrial applications, such as:
- Machinery: Frames, enclosures, and components.
- Automotive: Structural parts, trim, and heat sinks.
- Aerospace: Aircraft structural components and fittings.
Transportation Profiles: Utilized in the transportation sector, including:
- Trucks and Buses: Frames, bodies, and components.
- Rail Vehicles: Structural elements and interior fittings.
Consumer Profiles: Used in various consumer products, such as:
- Furniture: Frames, legs, and decorative elements.
- Electronics: Enclosures, heat sinks, and structural components.
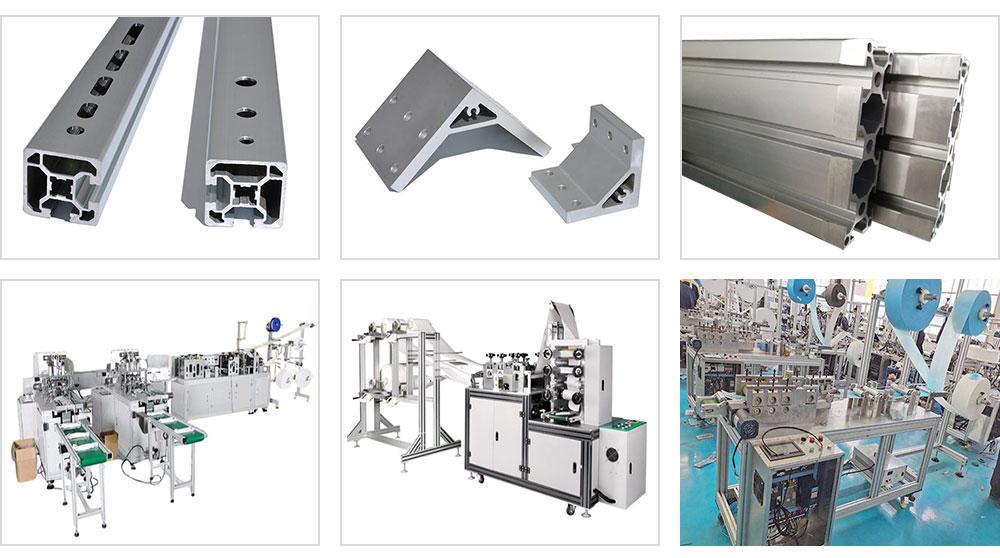

Understanding Aluminium Extrusion Profile Dimensions and Tolerances
Precise dimensional control is crucial for the successful application of aluminium extrusion profiles. Dimensional accuracy ensures proper fit, function, and aesthetic appeal in the final product. Key dimensional parameters include:
- Length: Overall length of the extrusion.
- Width: The maximum dimension perpendicular to the extrusion’s length.
- Thickness: The minimum dimension of the extrusion’s cross-section.
- Wall Thickness: The thickness of the extrusion’s walls.
- Corner Radii: The radii of the internal and external corners of the profile.
Tolerance Considerations
Tolerances define the permissible deviation from the specified dimensions. Factors influencing tolerance requirements include:
- Industry Standards: Relevant industry standards, such as those established by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), provide guidelines for acceptable tolerances.
- Customer Requirements: Specific customer requirements may dictate tighter or looser tolerances based on the application’s criticality.
- Assembly and Functionality: Tolerances must be carefully considered to ensure proper assembly and functionality of the final product.
- Aesthetics: In applications where aesthetics are important, tighter tolerances may be necessary to maintain a consistent and visually appealing appearance.
Techniques for Ensuring Dimensional Accuracy
- Precise Die Design: The accuracy of the extrusion die is paramount in determining the final dimensions of the profile.
- Careful Process Control: Maintaining consistent extrusion conditions, such as temperature and pressure, is essential for dimensional stability.
- Regular Quality Control: Implementing rigorous quality control measures, including dimensional inspections and testing, ensures adherence to specified tolerances.
Aluminium Extrusion Profile Recycling and Sustainability
Aluminium is a highly recyclable material, making it an environmentally friendly choice for various applications. The recycling process involves:
- Collection: Used aluminium extrusions are collected from various sources, such as scrap yards and manufacturing facilities.
- Sorting and Cleaning: The collected material is sorted and cleaned to remove impurities and contaminants.
- Melting: The cleaned aluminium is melted down in furnaces.
- Re-extrusion: The molten aluminium is re-extruded into new profiles, completing the recycling loop.
Benefits of Recycling Aluminium
- Energy Savings: Recycling aluminium requires significantly less energy than producing primary aluminium from bauxite ore.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Recycling minimizes the environmental impact associated with mining, refining, and processing bauxite.
- Resource Conservation: Recycling conserves natural resources and reduces the demand for virgin aluminium.
Industry Initiatives for Sustainability
- Sustainable Sourcing: Many aluminium producers prioritize the use of recycled content in their manufacturing processes.
- Life Cycle Assessments: Conducting life cycle assessments helps evaluate the environmental impact of aluminium extrusions throughout their entire lifecycle.
- Certifications and Eco-labels: Certifications, such as the Aluminium Stewardship Initiative (ASI) certification, recognize sustainable aluminium production practices.
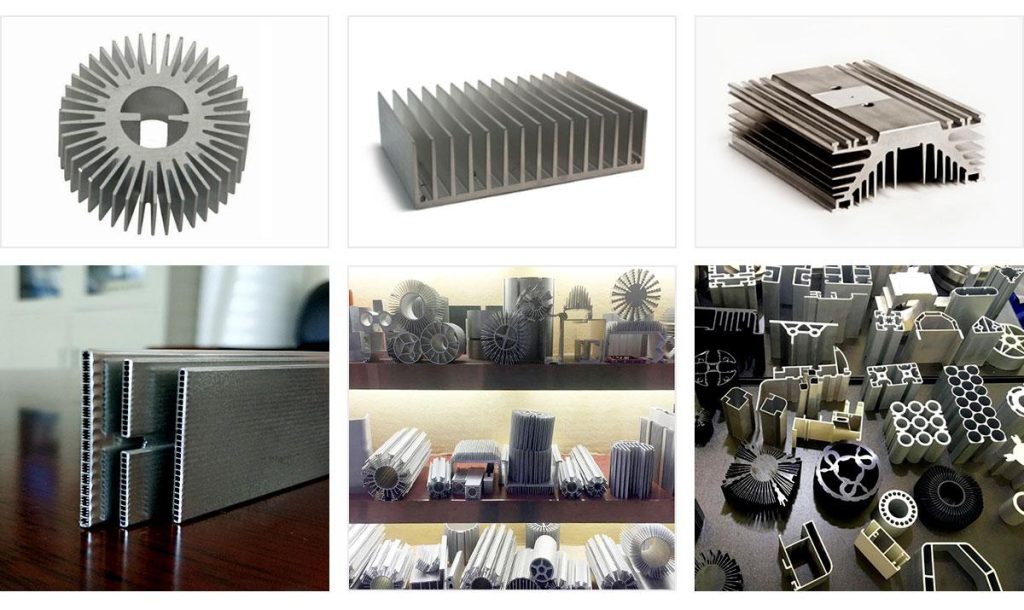
What Types of Aluminium Alloys are Used for Extrusion?
The choice of aluminium alloy significantly impacts the properties and performance of the extruded profile. Common aluminium alloys used for extrusion include:
- 6061: A versatile alloy known for its good strength, corrosion resistance, and weldability. It is widely used in various applications, including architectural, industrial, and transportation.
- 6063: A widely used alloy known for its excellent formability and good corrosion resistance. It is commonly used in architectural applications, such as window and door frames.
- 6082: A high-strength alloy suitable for applications requiring excellent mechanical properties. It is often used in structural applications, such as bridges and marine structures.
- 6005: A cost-effective alloy with good strength and corrosion resistance. It is commonly used in general-purpose applications, such as fencing and railings.
Alloy Properties and Applications
The choice of alloy depends on the specific requirements of the application, such as:
- Strength: Alloys with higher strength, such as 6082, are suitable for structural applications requiring high load-bearing capacity.
- Corrosion Resistance: Alloys with good corrosion resistance, such as 6061 and 6063, are preferred for outdoor applications and marine environments.
- Formability: Alloys with good formability, such as 6063, are easier to bend, shape, and form into complex geometries.
- Weldability: Alloys with good weldability, such as 6061, are suitable for applications requiring welding or joining processes.
As all mentioned above, aluminium extrusion profiles offer a versatile and sustainable solution for a wide range of applications. Understanding their types, dimensional considerations, recycling practices, and the properties of different aluminium alloys is crucial for selecting the appropriate profiles for specific needs. As the demand for sustainable materials continues to grow, aluminium extrusion technology offers a pathway to innovation and environmental responsibility, paving the way for a more efficient and sustainable built environment.