Aluminum foil, a versatile and essential material, finds extensive use in various industries due to its unique properties. However, not all aluminum foil is created equal. Two prominent types are heavy-duty aluminum foil and industrial aluminum foil. Understanding their similarities and differences is crucial for selecting the right material for specific applications. This article explores the commonalities and distinctions between heavy-duty aluminum foil and industrial aluminum foil, providing insights into their unique characteristics, production processes, and applications.

Similarities between Heavy-Duty Aluminum Foil and Industrial Aluminum Foil
Both heavy-duty aluminum foil and industrial aluminum foil share the same base material: aluminum. As forms of aluminum, they exhibit the inherent properties of this metal, which make them highly valuable across various industries. These properties include:
- Lightweight: Aluminum foil, in general, is lightweight, which makes it easy to handle and transport.
- Good Conductivity: Aluminum is an excellent conductor of electricity and heat, making aluminum foil suitable for applications requiring efficient energy transfer.
- Corrosion Resistance: Aluminum naturally forms a protective oxide layer on its surface, enhancing its resistance to corrosion. This property is beneficial in environments where the material is exposed to moisture and other corrosive agents.
Both heavy-duty aluminum foil and industrial aluminum foil are widely used in numerous industrial sectors due to their versatile nature. Their applications range from packaging and insulation to electronics and construction. Despite their different focuses, they both contribute significantly to the efficiency and functionality of various industrial processes.

Differences between Heavy-Duty Aluminum Foil and Industrial Aluminum Foil
1. Thickness and Applications
Heavy-Duty Aluminum Foil
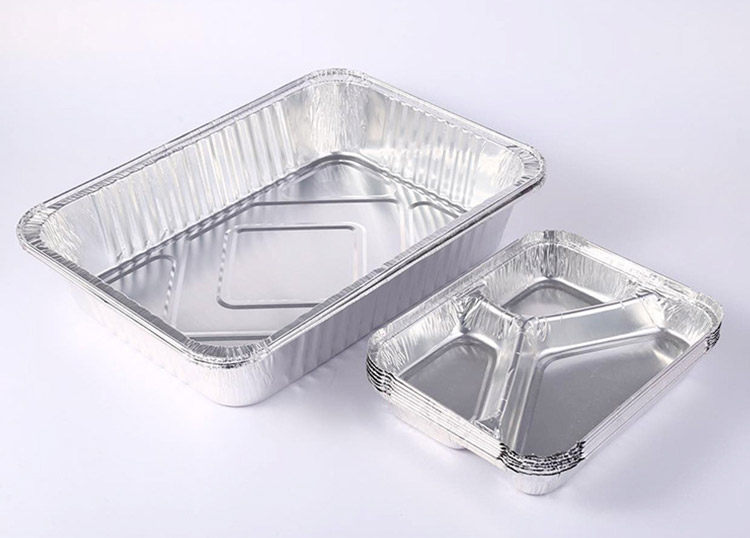
Heavy-duty aluminum foil is typically characterized by its greater thickness compared to standard and industrial aluminum foils. This increased thickness imparts higher strength and rigidity to the foil, making it suitable for applications that require robust materials. Common uses of heavy-duty aluminum foil include:
- Packaging: It provides strong and durable packaging solutions, especially for products that require enhanced protection against external elements.
- Transportation: Heavy-duty foil is used for lining and protecting goods during transportation, ensuring that they remain intact and uncontaminated.
Industrial Aluminum Foil
Industrial aluminum foil is a broader term that encompasses various thicknesses of aluminum foil tailored to meet diverse industrial needs. Unlike heavy-duty aluminum foil, which focuses on high-strength applications, industrial aluminum foil serves a wide range of purposes, including:
- Construction: Used for insulation, moisture barriers, and roofing materials.
- Automotive: Applied in heat shields, thermal insulation, and component wrapping.
- Electronics: Utilized in capacitor manufacturing, shielding, and insulation.
2. Production Processes
Heavy-Duty Aluminum Foil
The production of heavy-duty aluminum foil often involves specialized techniques to ensure the foil achieves the necessary thickness and strength. These processes may include multiple stages of rolling and annealing to enhance the material’s properties. The focus is on achieving a uniform thickness and robust mechanical properties to withstand demanding applications.
Industrial Aluminum Foil
Industrial aluminum foil production involves a variety of manufacturing processes tailored to specific industrial requirements. These processes may include different rolling techniques, heat treatments, and surface treatments to meet the diverse needs of construction, automotive, and electronic applications. The flexibility in production allows for a wide range of foil thicknesses and properties.

Unique Properties of Heavy-Duty Aluminum Foil
- Superior Strength and Corrosion Resistance: Heavy-duty foil often incorporates special alloy elements that significantly enhance its strength and resistance to corrosion. This makes it suitable for demanding environments like those encountered in aerospace applications or construction materials.
- Enhanced Sealing Performance: Heavy duty foil excels at creating strong yet peelable seals. This property proves invaluable for long-term storage and transportation, particularly when preventing oxygen, moisture, and other gases from entering the enclosed contents.
- Exceptional Solvent Resistance: Heavy duty foil demonstrates superior resistance to solvents. This allows it to be used for storing ultra-low-temperature compounds in organic solvents and for long-term room-temperature sample storage during transport.
- Wider Temperature Range: Heavy-duty foil maintains the integrity of its seals across a vast temperature spectrum, ranging from -200°C to 110°C. This adaptability makes it ideal for use in environments with extreme temperature fluctuations.
- High Load-Bearing Capacity: Due to its substantial weight and strength, heavy-duty foil can be employed in load-bearing structures. Applications include stage construction, bridge building, and mechanical manufacturing.
- Improved Processing Performance: While less malleable than standard aluminum foil, heavy-duty foil can still be processed through complex techniques like rolling, extrusion, and drawing. These processes ensure the foil retains its strength and stability despite its thickness.
How Processing Methods influence Aluminum Foil Performance?
The processing methods used in the production of aluminum foil, including rolling, annealing, and surface treatment, play a crucial role in determining its final performance characteristics.
Rolling: This process involves passing aluminum slabs through rollers, reducing their thickness. Factors like rolling temperature, speed, and tension significantly affect the foil’s microstructure and surface quality. Precise control of these parameters is crucial.
Annealing: Following rolling, the foil undergoes annealing, a heat treatment that relieves stresses induced during the rolling process. Annealing improves the foil’s processing and mechanical properties, making it more workable and enhancing its ductility. However, controlling temperature and time during annealing is essential to prevent oxidation and grain coarsening, which can negatively impact the foil’s performance.
Surface Treatment: To further enhance properties like corrosion and wear resistance, aluminum foil undergoes surface treatments. Common methods include:
- Chemical Polishing: This process removes a microscopic layer of the metal surface, resulting in a smoother and more reflective finish.
- Electrochemical Polishing: This method utilizes an electric current to selectively dissolve the metal surface, achieving an even smoother and brighter finish compared to chemical polishing.
- Anodizing: An electrochemical process that creates a protective oxide layer on the aluminum surface. This layer enhances corrosion resistance, and wear resistance, and can even improve the foil’s ability to be dyed or bonded to other materials.
The choice of surface treatment depends on the desired properties and the specific application of the aluminum foil.

Factors Affecting Surface Quality during Aluminum Foil Rolling
Several factors influence the surface quality of aluminum foil during the rolling process. These factors must be carefully controlled to achieve the desired properties and appearance.
- Rolling Oil Performance: The performance of rolling oil, including its oil film strength, viscosity, and lubrication, directly affects the surface quality of aluminum foil. Proper lubrication reduces surface scratches, and adhesion wear, and ensures flatness and smoothness.
- Roll Surface Quality: The roughness and hardness of the rolls used in the rolling process significantly impact the foil’s surface smoothness and microstructure. Regular maintenance and polishing of the rolls are essential to achieve high-quality surface finishes.
- Rolling Speed: The speed at which the aluminum foil is rolled affects the temperature of the rolls and the foil itself. Proper control of rolling speed is necessary to prevent surface defects such as oil spots, grooves, and variations in thickness.
- Rolling Pressure: The pressure applied during rolling influences the thickness uniformity and surface quality of the foil. Precise control of rolling pressure is critical to achieving the desired mechanical properties and appearance.
- Rolling Temperature: The temperature at which rolling occurs affects the ductility and rolling force of the aluminum foil. Maintaining the optimal rolling temperature is essential to prevent material deformation and ensure consistent thickness.
- Additives in Rolling Oil: Additives in rolling oil can improve lubrication and surface quality, reducing friction and wear during the rolling process. Selecting the right additives is crucial for achieving high-quality surface finishes.
- Lubrication Conditions: Proper lubrication conditions, including the type and amount of rolling oil used, play a significant role in reducing friction and wear during rolling. Adequate lubrication ensures smooth rolling and high-quality surface finishes.
- Precision of Rolling Equipment: The precision of rolling equipment, including the alignment and calibration of rollers, influences the plate shape and surface quality of aluminum foil. Regular maintenance and calibration of rolling equipment are essential to achieve consistent and high-quality products.

Conclusion
Understanding the differences and similarities between heavy-duty aluminum foil and industrial aluminum foil is essential for selecting the right material for specific applications. While both types of foil share common properties such as lightweight, good conductivity, and corrosion resistance, they differ in terms of thickness, production processes, and application fields. Heavy-duty aluminum foil, with its higher strength and sealing performance, is suitable for high-demand scenarios, while industrial aluminum foil offers versatility and adaptability for a wide range of industrial uses. Advances in processing methods and manufacturing technologies continue to enhance the performance and sustainability of aluminum foil, ensuring its relevance and importance in various industries.