The heart of any transformer lies in its windings, the coils of conductive material that facilitate the transfer of electrical energy between circuits. The choice between aluminum and copper wire for these windings is a critical decision that significantly impacts the transformer’s performance, cost, and efficiency. This article will explore the key factors to consider when selecting between these two materials.

The Role of Windings in a Transformer
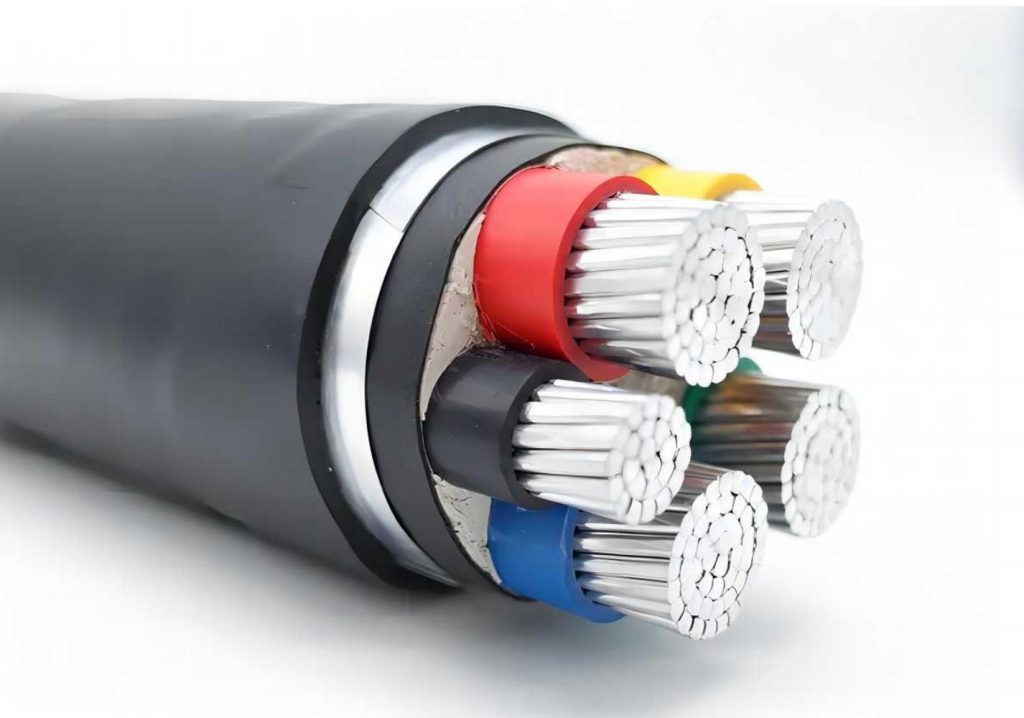
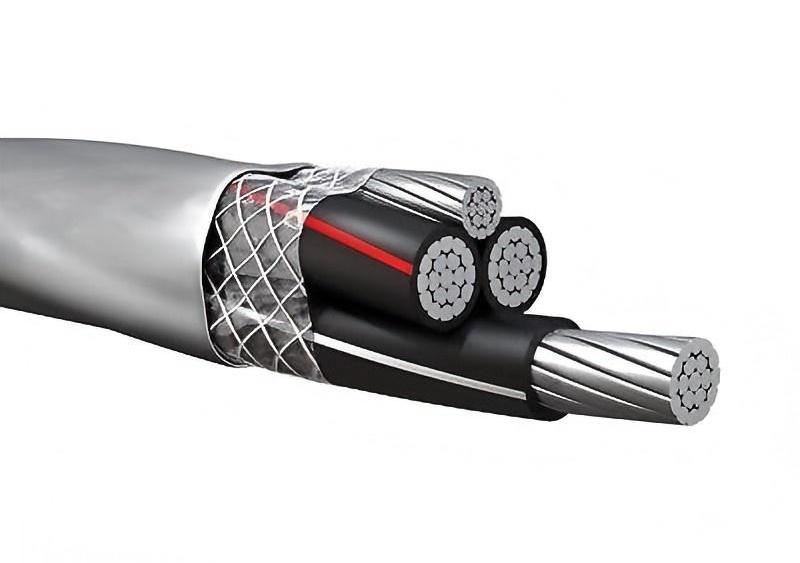
Transformer windings are essential components responsible for electromagnetic induction. They consist of multiple turns of conductive wire wrapped around a magnetic core. When an alternating current flows through the primary winding, it generates a changing magnetic field. This field induces a voltage in the secondary winding, enabling the transfer of electrical energy from one circuit to another.
The performance of a transformer is directly influenced by the properties of the wire used in its windings. Key factors affecting wire choice include:
- Conductivity: The ability of the wire to conduct electricity efficiently. Determines how efficiently the wire can carry current, affecting the overall performance of the transformer.
- Current-carrying capacity: The maximum amount of current the wire can safely handle without overheating.
- Heat dissipation: The wire’s ability to dissipate heat generated during operation. It is critical for maintaining transformer efficiency and preventing overheating.
- Mechanical Strength: Influences the wire’s ability to withstand physical stresses during operation and handling.
- Cost: The economic implications of using a particular wire material. Impacts the overall manufacturing and operational costs of the transformer.
These properties must be carefully evaluated when choosing between copper and aluminum wire for transformer windings.

Copper Wire: The Classic Choice
Copper has long been the preferred material for transformer winding due to its superior electrical conductivity and mechanical strength. Copper’s high conductivity allows for efficient current flow, minimizing energy losses and enhancing transformer performance. This makes copper an ideal choice for high-power transformers used in industrial and commercial applications.
In addition to its conductivity, copper boasts excellent mechanical strength, which enables it to withstand physical stresses during installation and operation. Copper is also resistant to corrosion, which contributes to the longevity of the transformer.
However, these benefits come at a higher cost. Copper is more expensive than aluminum, which can significantly increase the overall cost of manufacturing a transformer, especially for large transformers. Additionally, copper is heavier, which may pose challenges in transportation and installation.

Aluminum Wire: The Lightweight Challenger
Aluminum wire is gaining popularity as a cost-effective alternative to copper in transformer winding. While aluminum has lower electrical conductivity compared to copper, this can be compensated by using a larger cross-sectional area of aluminum wire to achieve similar current-carrying capacity.
Aluminum transformer winding wires come in various types such as round aluminum wire, rectangular (flat) aluminum wire, insulated aluminum wire etc., each designed to meet specific requirements for different transformer applications. Aluminum windings are often used in distribution transformers and residential applications where weight and cost are primary concerns.
One of the key advantages of aluminum is its lightweight nature. Aluminum is about one-third the weight of copper, making it an attractive option for transformers where weight is a concern. This can lead to easier handling and installation, as well as reduced structural requirements for supporting the transformer. Aluminum also offers good thermal performance, which is essential for maintaining transformer efficiency and preventing overheating.
However, it is less durable than copper and more susceptible to mechanical stress and oxidation, which may affect the long-term reliability of the transformer. Proper insulation and protection are crucial to mitigate this risk.
Factors Affecting the Decision
When choosing between copper and aluminum for transformer winding, several factors must be considered:
- Application Requirements: The specific needs of your transformer application, including power rating, size, and environmental conditions, will influence the choice of wire material. Larger transformers typically benefit from copper’s higher conductivity, while smaller transformers can effectively use aluminum.
- Cost analysis: Budget constraints play a significant role in the decision-making process. Aluminum is more cost-effective than copper, but long-term maintenance and performance must also be considered. Compare the initial cost of copper and aluminum wire against the potential long-term savings in energy consumption with copper.
- Weight considerations: Aluminum’s lighter weight can be advantageous for transportation and installation in certain applications where weight and space are limited.
- Environmental impact: Both copper and aluminum are recyclable, but the specific environmental footprint of each material should be considered.
- Industry Standards and Regulations: Compliance with industry standards and regulations is crucial, and the chosen material must meet these requirements.
Here we sort the considerations about when to choose aluminum or copper for transformer winding wire:
| Criteria | Choose Aluminum Wire | Choose Copper Wire |
| Electrical Conductivity | When slightly lower conductivity is acceptable | When maximum conductivity is essential |
| Cost Considerations | When cost efficiency is a priority | When budget allows for a higher material cost |
| Weight and Handling | When lightweight is crucial (e.g., large transformers) | When weight is not a major concern |
| Size and Space Constraints | When space is limited and requires larger wire sizes | When space is limited and high conductivity is needed |
| Thermal Performance | When good heat dissipation is needed but can be managed | When superior heat dissipation and higher operating temperatures are required |
| Mechanical Strength | When moderate mechanical strength is sufficient | When high mechanical strength and durability are necessary |
| Environmental Conditions | When corrosion resistance can be managed | When excellent corrosion resistance is critical |
| Application Type | Large-scale, cost-sensitive, or weight-sensitive projects | High-power, high-efficiency, and durability-focused projects |
| Longevity and Maintenance | When regular maintenance is acceptable | When long-term reliability with minimal maintenance is desired |
| Industry Standards | When industry standards allow for aluminum use | When strict industry standards demand copper |

In general, the choice between aluminum wire and copper wire should be comprehensively considered based on the specific needs, usage environment, and cost budget of the transformer. Copper wire is still the preferred choice for high-voltage and high-capacity transformers that pursue high performance and reliability; In low-voltage and small-capacity transformers that require high cost control, aluminum wire demonstrates its economic advantages. Both copper and aluminum wires play an indispensable role in the field of transformers, jointly promoting the development of power transmission and distribution technology.