Aluminum is one of the most versatile metals used in a variety of industries, and its applications in healthcare have grown significantly in recent years. In the medical field, aluminum alloys, particularly medical-grade aluminum, offer an ideal balance of lightness, durability, and biocompatibility. These properties make aluminum alloys indispensable in the manufacture of medical devices, implants, and pharmaceutical packaging. As technology advances, medical-grade aluminum alloys continue to play a crucial role in shaping the future of healthcare equipment and patient care.
This article will explore what makes aluminum alloys medical-grade, the key properties that set them apart, and their widespread applications in medical settings.
What Are Medical-Grade Aluminum Alloys?
Medical-grade aluminum alloys are specialized metal formulations specifically designed for use in medical environments. These alloys combine aluminum with other elements such as magnesium, silicon, copper, or zinc, which enhance specific properties like strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability. Unlike standard aluminum, which may not meet the stringent requirements of medical applications, medical-grade aluminum alloys undergo rigorous testing and certification processes to ensure their suitability for patient safety and device longevity.
Medical-grade aluminum alloys come from various series, each designed to meet specific requirements of strength, corrosion resistance, machinability, and biocompatibility. The 1000, 3000, and 5000 series are commonly used for packaging and non-implantable devices, while the 6000 series, particularly 6061, is highly favored for medical devices due to its strength and versatility. The 2000 and 7000 series are used in more specialized, high-strength applications, though they may require additional surface treatments for optimal performance in the medical field. The choice of alloy depends on the specific demands of the medical device, from structural integrity to resistance to bodily fluids and sterilization processes.

Key Properties of Medical-Grade Aluminum Alloys
- Biocompatibility: Biocompatibility is a key factor for any material used in medical devices, as it must not cause adverse reactions when in contact with the human body. Medical-grade aluminum alloys are highly biocompatible, making them suitable for implants, surgical tools, and other medical devices that directly interact with human tissue. The alloys’ inert nature helps prevent rejection or inflammation.
- Strength and Durability: Aluminum alloys used in medical applications are engineered to be strong and durable while remaining lightweight. This combination is especially important for devices that require both structural integrity and ease of handling, such as orthopedic implants or medical instruments.
- Corrosion Resistance: Corrosion resistance is critical in medical devices, which are often exposed to harsh conditions such as sterilization, body fluids, or chemicals. Medical-grade aluminum alloys have excellent corrosion resistance, ensuring that devices maintain their integrity over time, especially in environments requiring frequent sterilization.
- Lightweight: One of the most significant benefits of aluminum alloys is their lightweight nature, making them ideal for portable medical devices. For example, wheelchairs, prosthetics, and mobility aids made from aluminum are easier to handle for both medical professionals and patients.
- Ease of Machining and Formability: Aluminum alloys are easier to machine and shape compared to other metals like titanium or stainless steel. This allows manufacturers to create complex shapes required for various medical applications, such as custom implants or intricate medical instruments.
The combination of biocompatibility, strength, corrosion resistance, lightweight, and ease of machining makes medical-grade aluminum alloys an ideal choice for a wide range of medical applications. These properties ensure that medical devices and implants made from aluminum alloys are safe, durable, and effective in improving patient care and outcomes.

Common Applications of Medical-Grade Aluminum Alloys
Medical-grade aluminum alloys are utilized in various applications within the healthcare sector due to their favorable properties. From medical devices to pharmaceutical packaging, these alloys offer unmatched versatility.
Applications in Medical Devices and Equipment
Medical-grade aluminum alloys are widely used in the production of medical devices and equipment. Examples include diagnostic tools, surgical instruments, and therapeutic devices. For instance, endoscopes, surgical trays, and examination tables benefit from the lightweight yet durable nature of aluminum alloys, which ensures both portability and strength under the stress of medical procedures. The ability to sterilize these aluminum-based devices also contributes to their popularity in operating rooms and clinics.
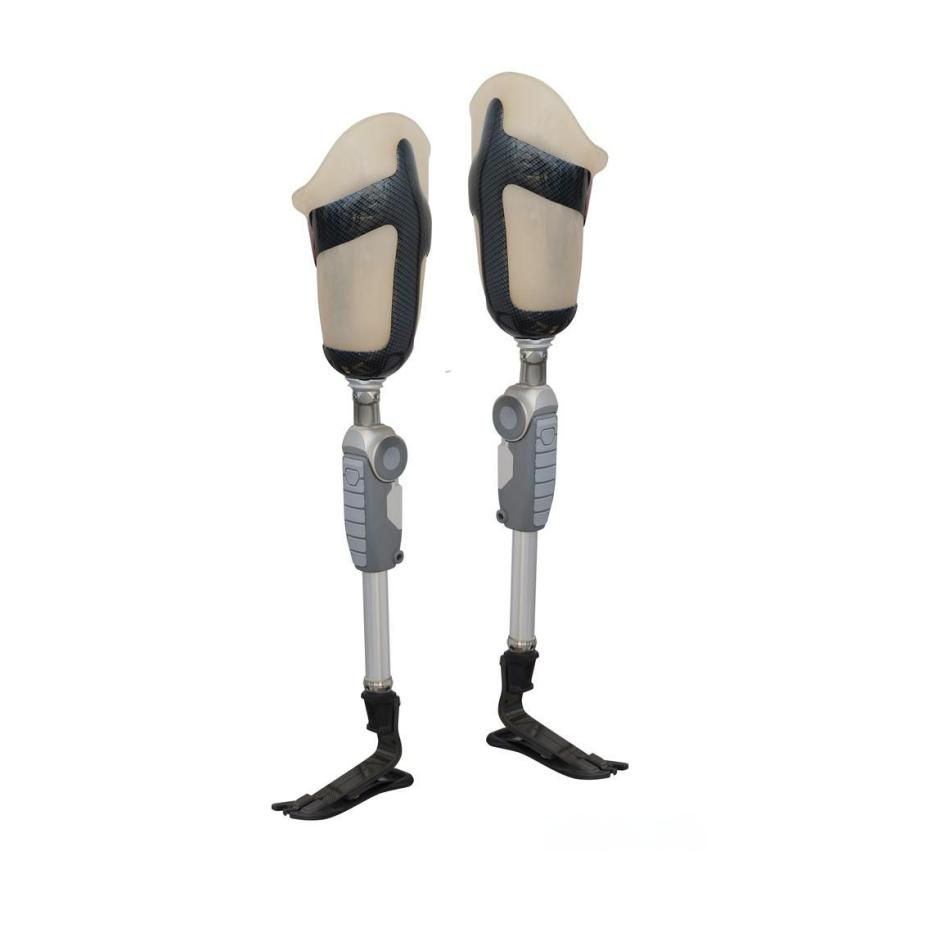
Applications in Implants and Prosthetics
One of the most significant applications of medical-grade aluminum alloys is in the manufacture of implants and prosthetics. Orthopedic implants, such as joint replacements, benefit from the lightweight and biocompatible nature of aluminum alloys. Although aluminum is not always used for long-term implants due to its limited strength compared to other materials like titanium, it is commonly used for temporary implants, such as fracture fixation devices, or in combination with other materials to enhance their properties.
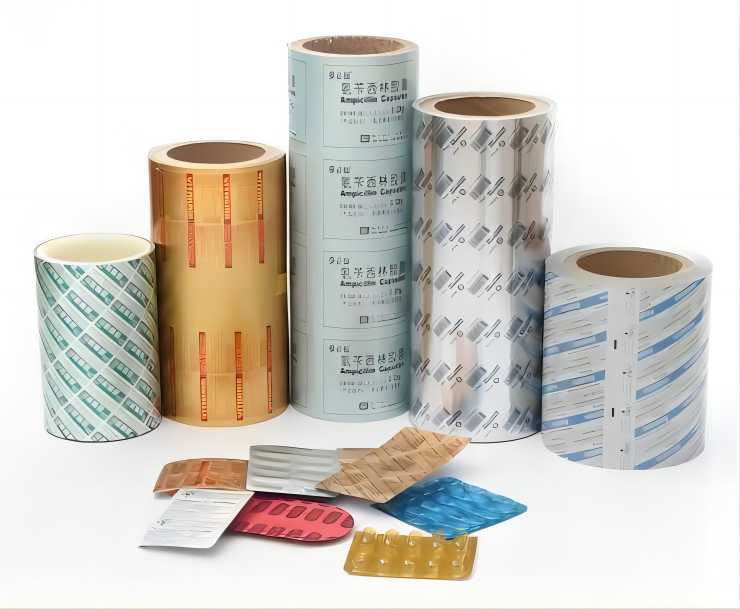

Pharmaceutical Packaging
Aluminum alloys play an essential role in pharmaceutical packaging, particularly in blister packs and foil seals. The alloy’s corrosion resistance and barrier properties ensure that medications remain protected from moisture, light, and air, which could compromise their potency. Aluminum foil is commonly used to package tablets, capsules, and other forms of medication, ensuring both protection and ease of use.
Hospital and Laboratory Equipment
In hospitals and laboratories, aluminum alloys are used to produce a wide variety of essential equipment, including mobile carts, diagnostic machines, and laboratory stands. Aluminum’s strength-to-weight ratio makes it ideal for items that require both durability and mobility. The alloy is easy to clean and sterilize, making it perfect for environments that must maintain high levels of hygiene.
The applications of medical-grade aluminum alloys are diverse, ranging from surgical tools and implants to pharmaceutical packaging and hospital equipment. These alloys provide the necessary strength, safety, and efficiency for a wide variety of medical uses, ensuring that healthcare providers can deliver optimal care to patients.
Here we make a conclusion of the common medical-grade aluminum alloys and their uses:
| Series | Alloy | Key Characteristics | Common Uses |
| 1000 Series | 1050 | High corrosion resistance Excellent formability Good conductivity | Pharmaceutical packaging (blister packs) Medical trays and containers |
| 2000 Series | 2011 | High strength Moderate corrosion resistance Excellent machinability | Medical tools and devices that require strength but not constant exposure to bodily fluids |
| 3000 Series | 3003 | Good corrosion resistance Moderate strength Good formability | Medical packaging Non-implantable components Trays and containers |
| 5000 Series | 5052 | Excellent corrosion resistance Moderate to high strength Good weldability | Medical equipment Orthopedic devices Prosthetics frames Medical equipment requiring corrosion resistance |
| 6000 Series | 6061 | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio Good corrosion resistance Excellent machinability | Surgical tools Prosthetics Frames for medical devices Implantable medical devices |
| 6000 Series | 6063 | Good strength Excellent formability and finish Moderate corrosion resistance | Medical frames Lightweight medical devices Hospital and laboratory equipment |
| 7000 Series | 7075 | Very high strength Moderate corrosion resistance Requires additional surface treatment for medical use | High-strength medical components Surgical instruments Orthopedic applications |
The choice of alloy depends on the specific demands of the medical device. Medical-grade aluminum alloys are specially formulated to meet the rigorous standards required for use in medical devices, implants, and pharmaceutical packaging.

Challenges of Aluminum Alloys in Medical Applications
While aluminum alloys offer numerous advantages in medical applications, there are certain challenges that need to be addressed:
- Fatigue Strength: Aluminum alloys may exhibit lower fatigue strength compared to other materials, such as titanium. This can limit their use in high-stress applications.
- Wear Resistance: In some cases, aluminum alloys may have lower wear resistance compared to other metals. This can affect the long-term durability of medical devices.
To overcome these challenges, researchers and engineers continue to develop innovative alloy compositions and surface treatments to enhance the properties of aluminum alloys. By addressing these limitations, aluminum alloys have the potential to become even more widely used in the medical field.