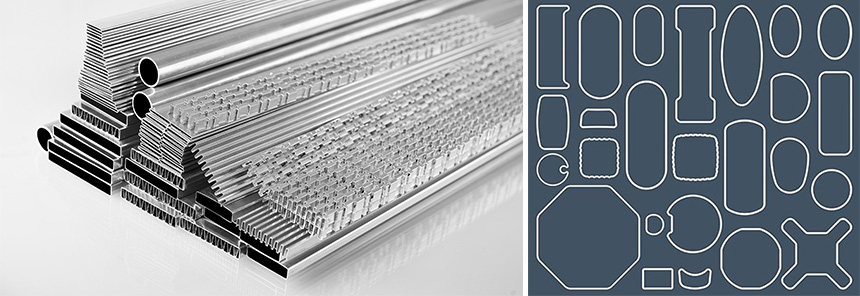
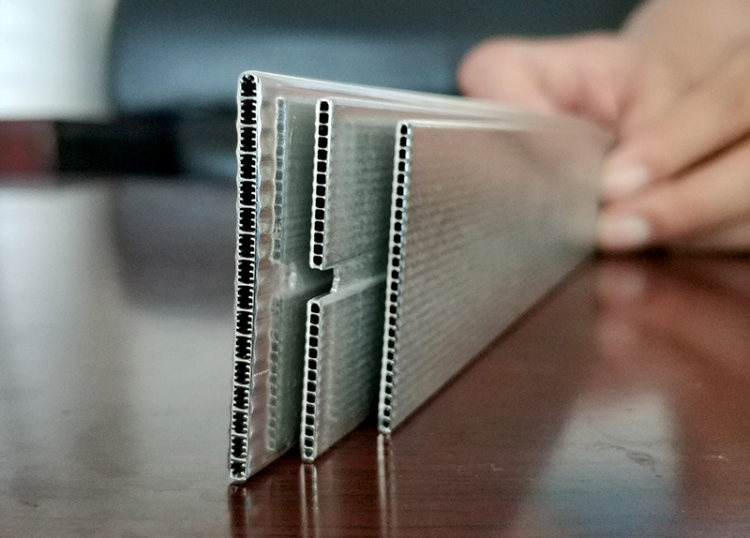
Structural aluminum tubes, prized for their lightweight nature, high strength, and corrosion resistance, find extensive applications across diverse sectors including construction, machinery, and aerospace. As industrial demands diversify and technology advances, the application scenarios for structural aluminum tubes continue to expand, placing higher demands on their shapes, connection methods, and post-connection inspections. This article delves into the common shapes of structural aluminum tubes, their connection techniques, and the inspection methods employed after connection, providing practical engineering references.
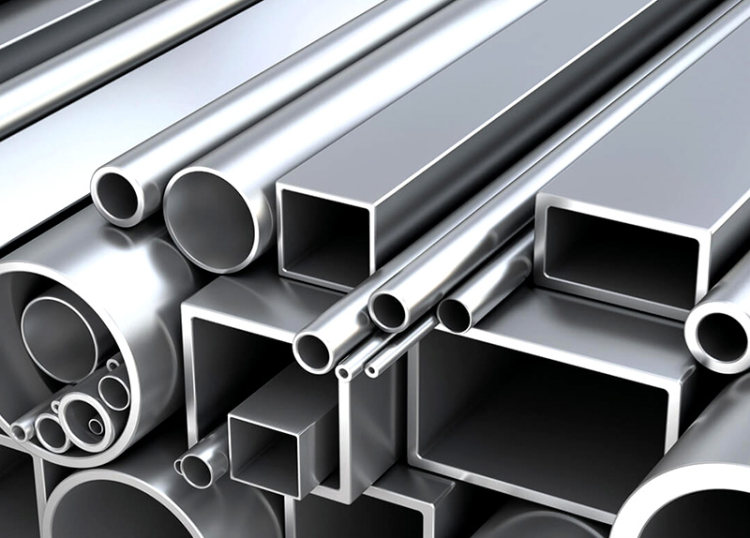

Common Shapes of Structural Aluminum Tubes
The shape of a structural aluminum tube plays a crucial role in determining its performance across different applications. Various shape designs cater to specific engineering needs, optimizing structural performance. Below are several common shapes of structural aluminum tubes and their respective characteristics:
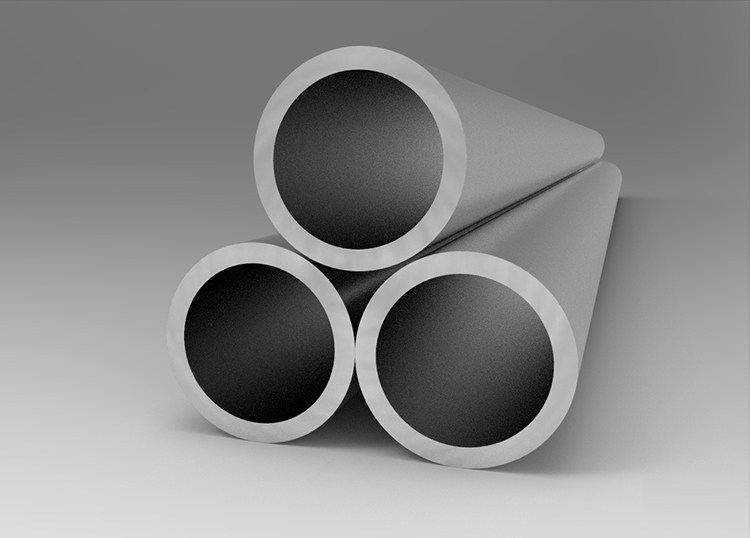
1. Round Tubes
Round aluminum tubes are the classic and most widely used form. They are primarily employed in fluid transport, framework supports, and pipeline systems. Key characteristics include:
- Uniform Strength Distribution: A round cross-section distributes stress evenly across the tube, making it ideal for applications where pressure needs to be handled from all directions.
- Manufacturing Simplicity: The production process for round tubes is relatively simple and cost-effective, contributing to their widespread use.
- Versatility: Due to these properties, round tubes are used extensively in various industries, including automotive, construction, and industrial machinery.

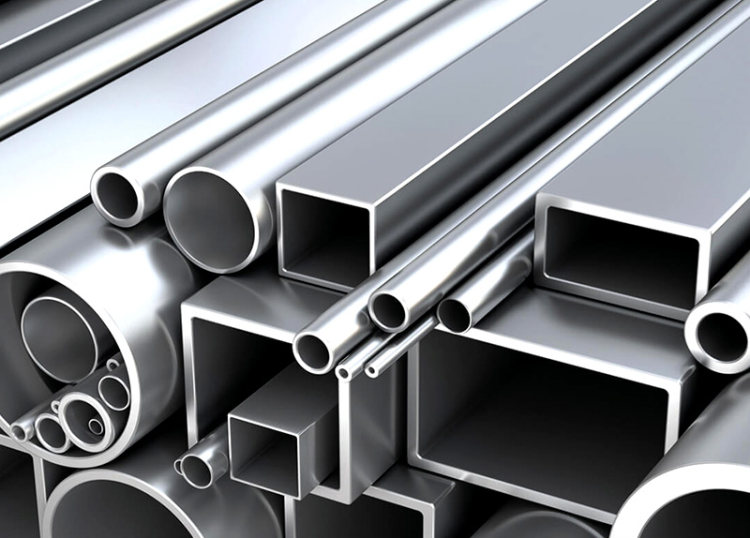
2. Structural Aluminum Rectangular Tubes
Rectangular aluminum tubes are commonly used in structures that require specific directional strength. Their distinct shape offers several advantages:
- Increased Bending and Torsional Strength: Compared to round tubes, rectangular tubes are better at resisting bending and twisting forces, making them suitable for heavy-duty structural applications like building frames and mechanical equipment supports.
- Design Flexibility: The length and width ratio can be adjusted based on specific engineering needs, providing more flexibility in design.
- Efficient Load Distribution: Rectangular tubes are often employed in applications where loads are applied in specific directions, such as roof supports or wall structures in buildings.
3. Structural Aluminum Square Tubes
Square aluminum tubes offer several distinct advantages over round tubes in certain applications:
- High Bending and Torsional Resistance: Similar to rectangular tubes, square tubes exhibit enhanced resistance to bending and twisting forces, providing better structural stability under load.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Square tubes are often used in modern architecture and design for their clean, geometric appearance.
- Applications: They are widely used in structural framing, scaffolding, and other applications where strength and aesthetics are crucial.
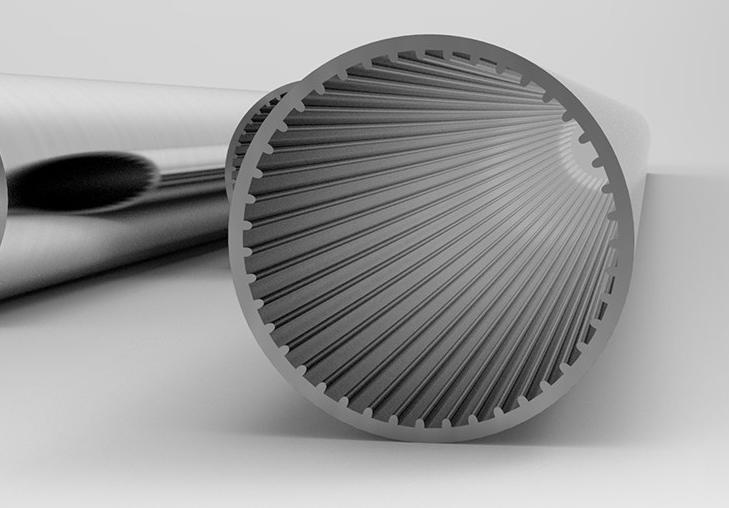
4. Special-Shaped Tubes
With advancements in manufacturing techniques, special-shaped aluminum tubes have become increasingly popular in industries such as aerospace and automotive manufacturing. These tubes can be tailored to meet specific functional needs:
- Customizability: Shapes such as elliptical or triangular tubes can be designed to optimize fluid dynamics or provide specialized structural connections.
- High-Performance Applications: In fields like aerospace and automotive manufacturing, special-shaped tubes are used to enhance product performance and efficiency.

5. Aluminum Profiles
Aluminum profiles are an extension of structural aluminum tubes and are created by extruding aluminum into various complex cross-sectional shapes. They offer significant design flexibility:
- Versatility: Profiles can be customized to meet specific needs, making them ideal for industries requiring highly specialized shapes.
- Ease of Assembly: Aluminum profiles are often used with various connectors to create frames, workstations, assembly lines, and other industrial applications.
Connection Methods for Structural Aluminum Tubes
The method chosen for connecting structural aluminum tubes directly influences the strength, stability, and reliability of the structure. Below are several common connection methods:
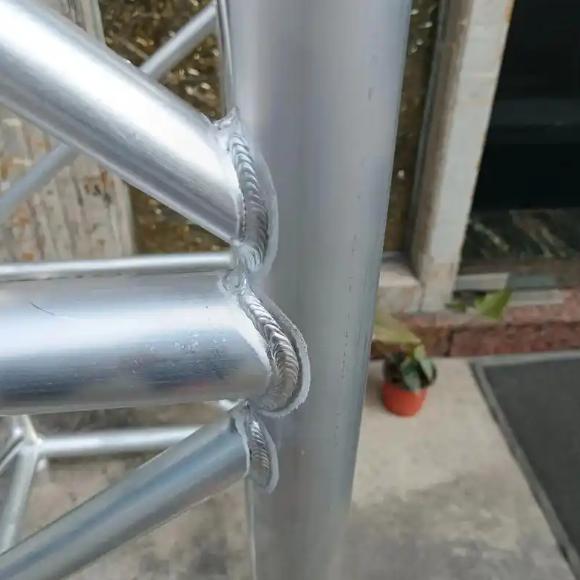
1. Welding
Welding is a high-strength connection method suitable for applications requiring robust and permanent bonds:
- Types of Welding: Common methods for aluminum alloy welding include Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding and Metal Inert Gas (MIG) welding.
- Specialized Techniques: Aluminum welding requires specialized skills and equipment to avoid defects such as porosity or cracks. The heat-affected zone (HAZ) can weaken the material, often necessitating post-weld heat treatment.
- Applications: Welding is typically used in permanent structural connections, where dismantling is not required.
2. Bolted Connections
Bolted connections are a versatile, detachable option suitable for applications that require frequent disassembly or maintenance:
- Flexibility: Bolted joints are easy to assemble and disassemble, making them ideal for modular construction.
- Strength Considerations: While bolted connections are relatively simple, they can suffer from loosening over time, which may affect the integrity of the joint.
- Material and Torque Specifications: The selection of bolts, their material properties, and the torque used during fastening are crucial to ensuring a reliable connection.
3. Riveting
Riveting is another permanent connection method, ideal for connecting thin-walled aluminum tubes:
- High Strength: Riveted joints offer strong connections, though they cannot be easily undone.
- Application: Riveting is often used in aerospace and automotive industries, where permanent joints are necessary.
- Precision: Proper control of rivet installation force is essential to prevent deformation or damage to the aluminum tube.
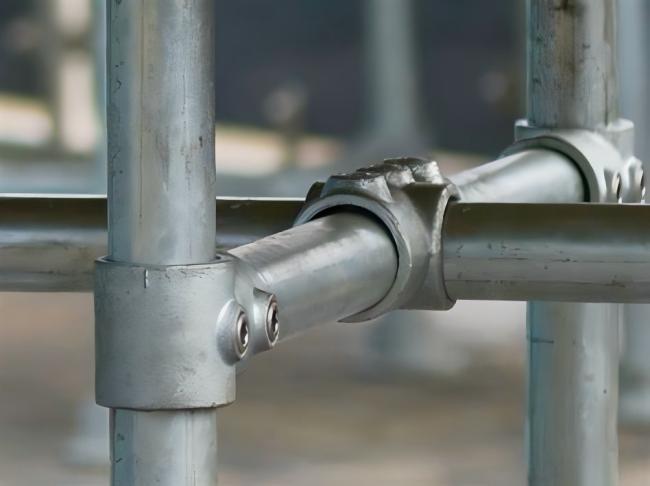

4. Compression Fittings
Compression fittings are a quick and efficient method of connecting aluminum tubes, particularly for piping applications:
- Simple Installation: These fittings, often used in fluid transport systems, provide an easy way to connect aluminum tubes without welding or threading.
- Applications: They are commonly found in low-pressure pneumatic or hydraulic systems, where sealing and ease of installation are essential.
5. Aluminum Profile Connectors
Aluminum profile connectors, such as T-nuts, brackets, and fasteners, are often used in modular construction systems:
- Flexibility: These connectors allow for easy, customizable design and assembly of frames, workstations, or conveyor systems.
- Quick Assembly: The use of standard connectors and profiles makes construction and adjustment quick and easy.
Post-Connection Inspections of Structural Aluminum Tubes
To ensure the quality and safety of structural aluminum tube connections, a series of inspections are necessary. Below are several common techniques used to verify the quality of aluminum tube joints:
1. Visual Inspection
Visual inspection is the most basic and first level of testing, aimed at identifying obvious defects:
- Inspection Scope: The inspector looks for cracks, deformation, porosity, or inclusions in the connection area.
- Limitations: While effective at detecting visible issues, visual inspection does not detect internal defects.
2. Dimensional Measurement
Dimensional measurement ensures that the connected tubes meet specified design criteria:
- Tools: Tools such as calipers, micrometers, and angle gauges are used to measure key dimensions, including length, width, thickness, and angles.
- Accuracy: This ensures that the connection meets all specifications and maintains the structural integrity of the assembly.

3. Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)
Non-destructive testing methods allow for internal defect detection without compromising the integrity of the material:
- Methods: Common NDT methods include ultrasonic testing, radiographic inspection, magnetic particle testing, and dye penetrant testing.
- Applications: NDT is particularly useful in high-performance applications such as aerospace and heavy machinery, where safety is critical.
4. Mechanical Testing
Mechanical testing evaluates the strength and performance of the aluminum tube connection under load:
- Tests: Tensile, bending, and shear tests are used to assess the load-bearing capacity of the joint.
- Verification: These tests ensure that the connection can withstand the applied forces without failure.
5. Leak Testing
For fluid transport systems, leak testing ensures the connection’s ability to maintain pressure without leaks:
- Methods: Common techniques include pressure testing, vacuum testing, and the use of leak detection instruments.
- Importance: Leak testing is essential for applications like piping systems, where the risk of fluid loss could result in system failure or safety hazards.
Summary
Structural aluminum tubes, with their superior performance and diverse applications, play a vital role in modern industry. Selecting the appropriate shape, connection method, and inspection technique is crucial for ensuring the effectiveness of structural aluminum tube applications. With continuous advancements in manufacturing technology, the application fields of structural aluminum tubes will further expand, bringing more possibilities to the development of various industries. When considering the size of the material, it is also important to check the structural aluminum tube sizes that are needed for the project.