Aluminum has become an indispensable material in the construction industry, owing to its exceptional properties that make it an ideal choice for a wide range of structural applications. Lightweight, durable, and corrosion-resistant, aluminum has gained prominence in modern architecture and construction. In this article, we’ll explore the different types of alloys used in construction and the design considerations for aluminum structures.
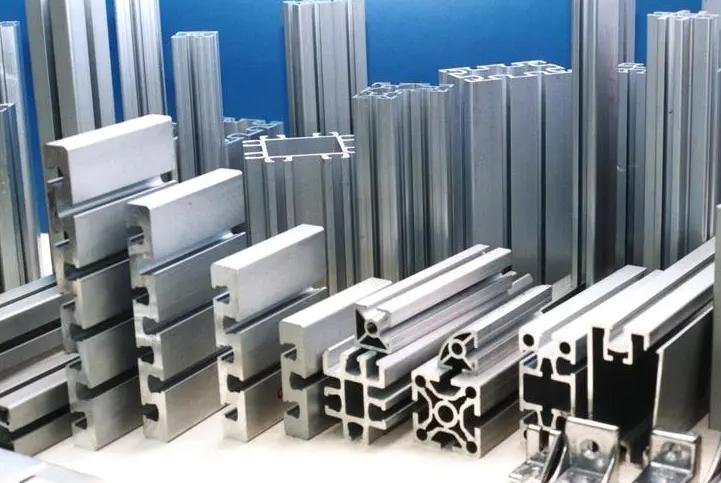

What Are the Types of Aluminum Alloys Used in Construction?
There are many different types of aluminum alloys used in construction, each with its own unique properties. Some of the most common alloys include:
- 3000 series alloys: These alloys are the most common type of aluminum alloy, particularly 3003 and 3105. They are known for their good formability and weldability. They are often used in applications where these properties are important, such as cans, foil, and tubing.
- 5000 series alloys: Alloys in the 5000 series, like 5052 and 5083, are known for their high corrosion resistance and are used in marine and offshore applications. They are also suitable for architectural elements exposed to harsh environmental conditions such as siding, roofing, and windows.
- 6000 series alloys: The 6000 series alloys, such as 6061 and 6063, are among the most popular choices for construction applications. They offer excellent strength, corrosion resistance, and weldability. These alloys are used for a variety of structural components, including beams, columns, and window frames.
- 7000 series alloys: These alloys are even stronger and more durable than 6000 series alloys. They are often used in applications where high strength and weight savings are critical, such as aircraft and spacecraft. They are less commonly used in general construction but can be employed in specialized projects where high strength is essential.

What are the Design Considerations for Aluminum Structures?
There are a number of design considerations that need to be taken into account when designing aluminum structures. These include:
- Strength: Aluminum is a lightweight metal, but it can be very strong when alloyed with other metals such as copper, magnesium, and zinc. The strength of the aluminum alloy that is chosen will depend on the loads that the structure will be subjected to.
- Stiffness: Aluminum structures can be very stiff, but they can also be flexible, depending on the shape and thickness of the aluminum members. The stiffness of the structure will need to be considered to ensure that it can withstand the expected loads without deforming excessively.
- Fatigue: Aluminum is susceptible to fatigue failure, which can occur when the metal is subjected to repeated cyclic loading. When designing aluminum structures, it is important to consider the fatigue life of the structure to ensure that it will not fail prematurely.
- Buckling: Aluminum columns can buckle under compressive loads. When designing aluminum columns, it is important to consider the buckling load to ensure that the columns will not buckle prematurely.
- Corrosion: Aluminum is generally resistant to corrosion, but it can corrode in certain environments, such as marine environments or environments with high levels of pollution. When designing aluminum structures, it is important to consider the potential for corrosion and take steps to protect the structure from corrosion if necessary.
- Fire resistance: Aluminum has a low melting point, so it is not as fire resistant as some other metals, such as steel. When designing aluminum structures, it is important to consider the fire resistance of the structure and take steps to protect the structure from fire if necessary.
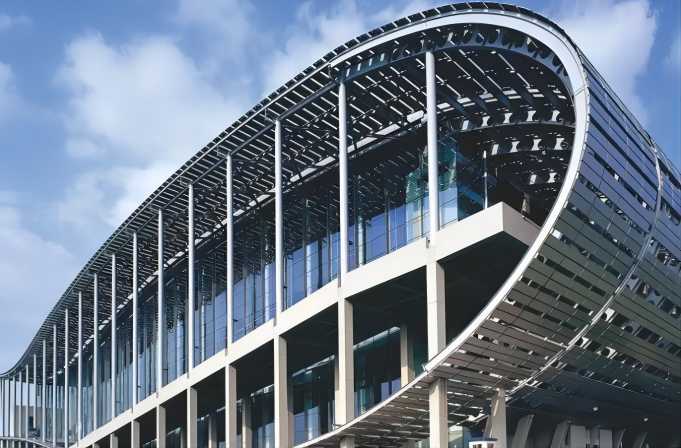

In addition to the general design considerations listed above, there are a number of specific design considerations that need to be taken into account when designing different types of aluminum structures. For example, when designing aluminum buildings, it is important to consider the following factors:
- Wind loads: Aluminum buildings are susceptible to wind damage, so it is important to design the building to withstand the expected wind loads.
- Snow loads: Aluminum buildings are also susceptible to snow damage, so it is important to design the building to withstand the expected snow loads.
- Seismic loads: Aluminum buildings are susceptible to seismic damage, so it is important to design the building to withstand the expected seismic loads.
Here are some additional tips for designing aluminum structures:
- Use extruded aluminum shapes whenever possible. Extruded shapes are stronger and stiffer than rolled shapes, and they can be used to create complex shapes that would be difficult or impossible to fabricate using rolled shapes.
- Design for continuous load paths. A continuous load path is a path that allows loads to be transferred directly from one member of the structure to another without causing any bending or deflection in the members. Designing for continuous load paths will help to reduce the risk of fatigue failure.
- Use gusset plates to connect aluminum members. Gusset plates are triangular or rectangular plates that are used to connect two or more members together. Gusset plates help to distribute loads evenly between the members and reduce the risk of fatigue failure.
- Use corrosion-resistant fasteners. Aluminum is susceptible to galvanic corrosion, which can occur when aluminum is in contact with other metals. When designing aluminum structures, it is important to use corrosion-resistant fasteners, such as stainless steel fasteners, to prevent galvanic corrosion.
By following these tips, engineers can design aluminum structures that are strong, stiff, durable, and corrosion-resistant.
Conclusion
In conclusion, aluminum’s versatility and unique properties have made it an essential material in modern construction. Its different alloys cater to a wide range of applications, and when properly designed, aluminum structures can be cost-effective, durable, and visually striking. As the construction industry continues to evolve, aluminum’s role is likely to expand, contributing to the development of innovative and sustainable buildings.