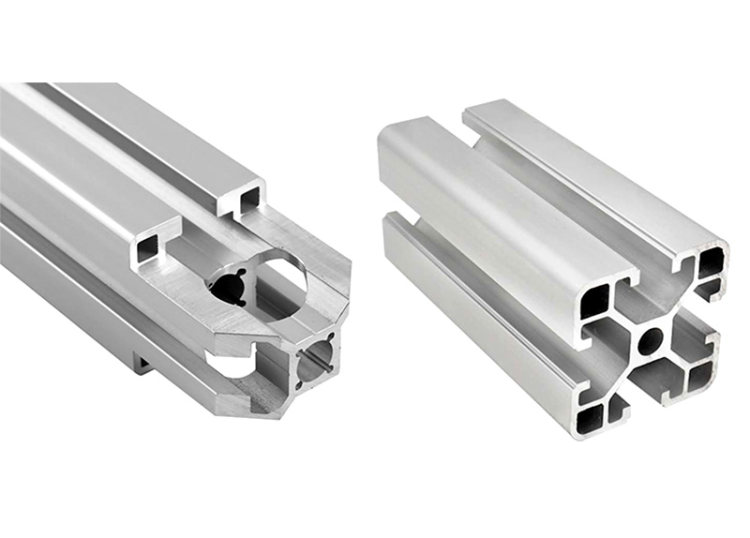
To manufacture a good set of aluminum extrusion die, not only good processing equipment and skilled extrusion die manufacturing workers, but also a very important factor is to have a good extrusion die design. The aluminum extrusion die not only needs to fully understand the customer’s requirements but also requires the die designer to have an understanding of the extrusion machine, extrusion die structure, and processing technology, as well as the processing capacity of the factory.
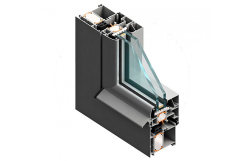
An extrusion die is a thick steel disk with an opening — and malleable aluminum alloy passes through it during the extrusion process.
The opening in the die matches the cross-sectional profile that’s specified by the extrusion designer.
Familiar with the dimensions and tolerances of aluminum
The size and deviation of aluminum are determined by extrusion dies, extrusion equipment, and other related process factors.
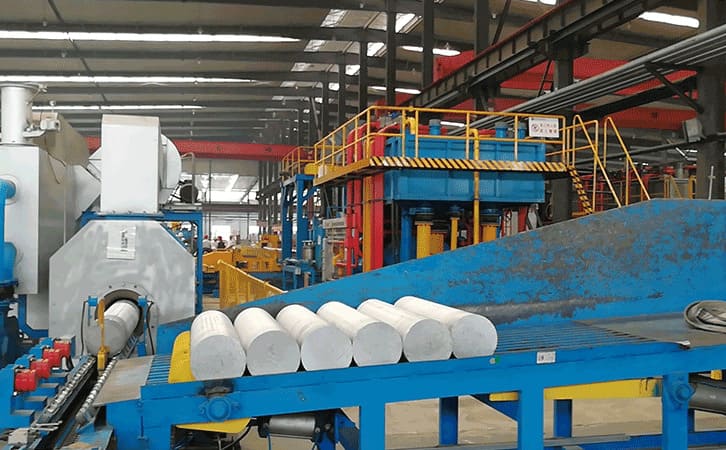
Choosing the Right Aluminum Extrusion Press Tonnage
The selection of the tonnage of the extruder is mainly determined according to the extrusion ratio. If the extrusion ratio is lower than 10, the mechanical properties of the aluminum product are low; if the extrusion ratio is too high, the aluminum product is prone to defects such as surface roughness and angle deviation. The extrusion ratio of solid aluminum is often recommended to be around 30, and that of hollow aluminum is around 45.

Determine the extrusion die shape
The external dimensions of the extrusion die to refer to the outer diameter and thickness of the extrusion die. The external dimensions of the extrusion die are determined by the size, weight, and strength of the profile section.
Determination of Die Hole Size of Extrusion Die
For aluminum with a large difference in wall thickness, the difficult-to-form thin-walled parts, and edge sharp corners should be appropriately increased in size; for flat-width thin-walled profiles with large width-thickness ratios and die holes of wall plate profiles, the stringer part should be The size can be designed according to the general profile, and the size of the web thickness, in addition to the factors listed in the formula, still need to consider the elastic deformation and plastic deformation of the extrusion die and the overall bending, distance from the extrusion cylinder and other factors. In addition, the extrusion speed, the presence or absence of traction devices, etc. also have a certain influence on the size of the die hole.
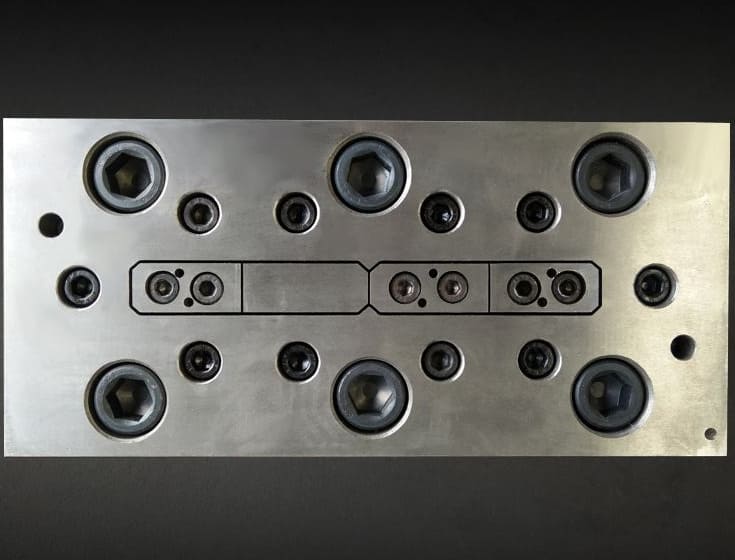

Reasonably adjust the flow speed of aluminum alloy
A reasonable adjustment of the flow rate of aluminum metal is to try to make every particle on the aluminum section flow out of the die hole at the same speed. When designing the extrusion die, try to use a porous symmetrical arrangement. According to the shape of the aluminum material, the difference in wall thickness of each part, the difference in specific circumference, and the distance from the extrusion cylinder, the sizing belt of unequal length is designed. Generally speaking, the thinner the wall thickness of the aluminum material, the larger the perimeter, the more complex the shape, and the farther it is from the extrusion cylinder, the shorter the sizing belt here. If it is still difficult to control the flow rate of the aluminum metal with the sizing belt, the section shape of the aluminum material is particularly complex, the wall thickness is very thin, and the flow-promoting angle or the guide cone can be used to accelerate the flow of the aluminum metal in the part far away from the middle. For those parts with a much thicker wall or very close to the extrusion barrel, the obstruction angle should be used to supplement the obstruction to slow down the flow rate. In addition, process balance holes, process allowances, front chamber molds, guide molds, and changes in the number, size, shape, and position of the flow distribution holes can be used to adjust the flow rate of aluminum metal.
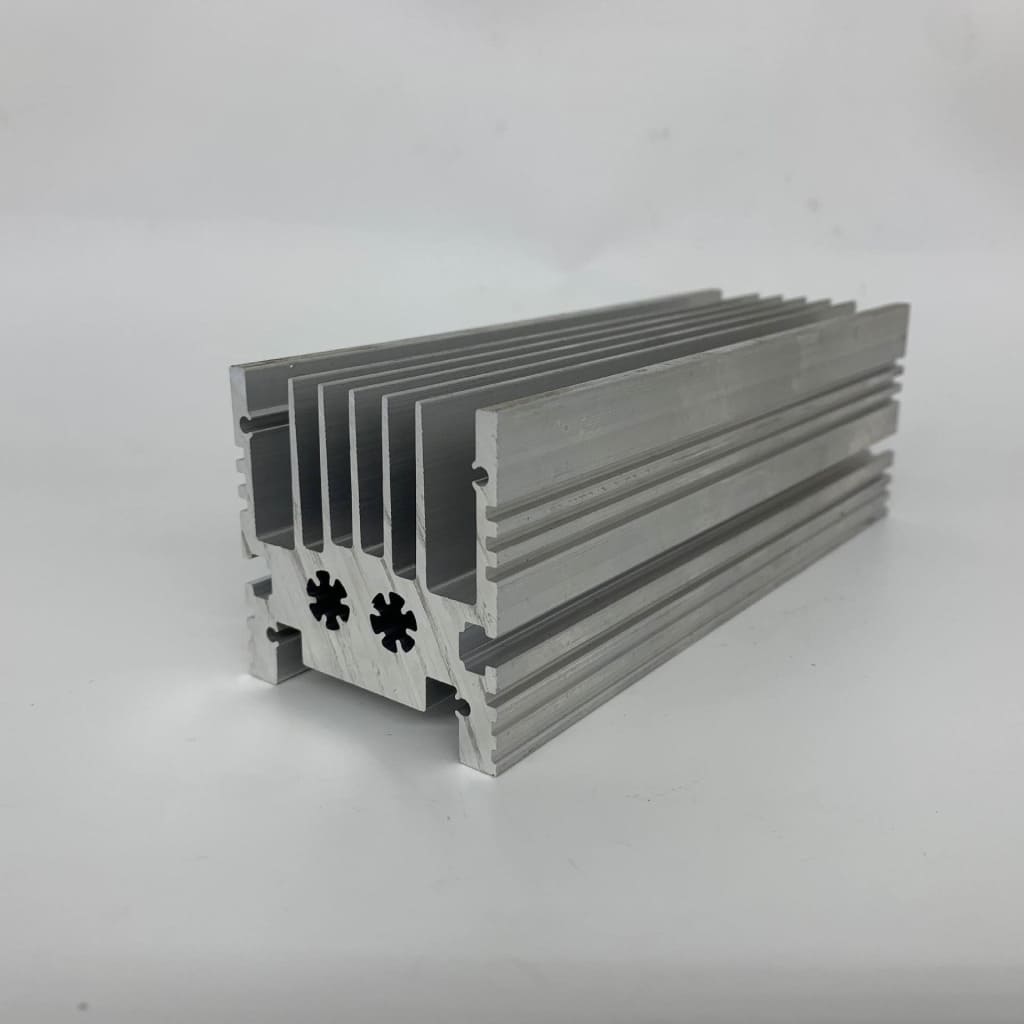

Extrusion die strength check
Due to the harsh working conditions of the die during the extrusion of aluminum, die strength is a very important issue in die design. In addition to arranging the position of the die hole reasonably, selecting the appropriate die material, and designing a reasonable die structure and shape, it is also very important to accurately calculate the extrusion force and check the allowable strength of each dangerous section. At present, there are many formulas for calculating the extrusion force, but the modified Berlin formula still has engineering value. The upper limit solution of the extrusion force also has an applicable good value, and it is relatively simple to use the empirical coefficient method to calculate the extrusion force. As for the check of mold strength, it should be carried out separately according to the type of product, mold structure, etc. Generally, flat molds only need to check shear strength and flexural strength. Tongue molds and flat shunt molds need to check shear, bending, and compressive strengths. Tongue and needle tip parts also need to consider tensile strength. In recent years, the finite element method can be used to analyze the force and check the strength of the particularly complex mold.
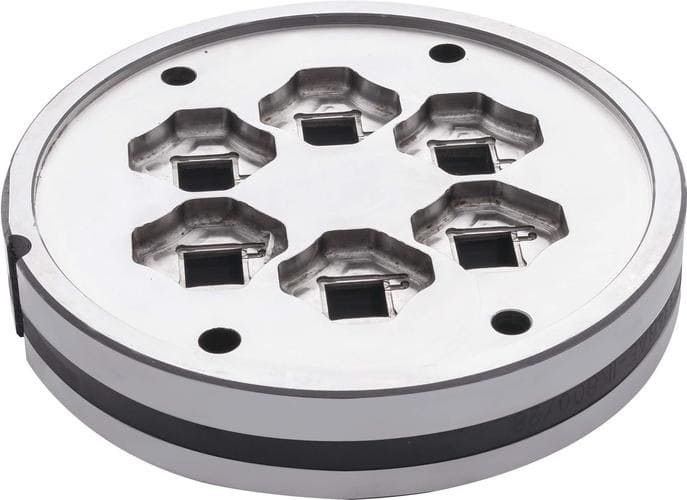

Reasonable working belt size
It is much more complicated to determine the working belt of the split die combination than the working belt of the half mold. Not only to consider the wall thickness difference of the profile, and the distance between the middle and the surface but also to consider the situation that the die hole is shielded by the split bridge. For the die hole under the shunt bridge, due to the difficulty of metal flowing in, the working belt must be considered thinner. When determining the working belt, first of all, find where the wall thickness of the profile under the shunt bridge is thin, that is, where the metal flow resistance is large. The small working belt here is set to be twice the wall thickness, and the wall thickness is thicker or where the metal is easy to reach. , The working belt should be properly thickened, generally according to a certain proportional relationship, plus a correction value for easy flow.
Die hole empty knife structure and size
The die-hole empty knife is the structure of the cantilever support at the outlet end of the die-hole working belt. When the wall thickness of the aluminum material is greater than or equal to 2mm, the straight hollow knife structure that is easier to process can be used; when the wall thickness of the aluminum material is less than 2mm, the inclined hollow knife can be selected to be processed at the cantilever.